
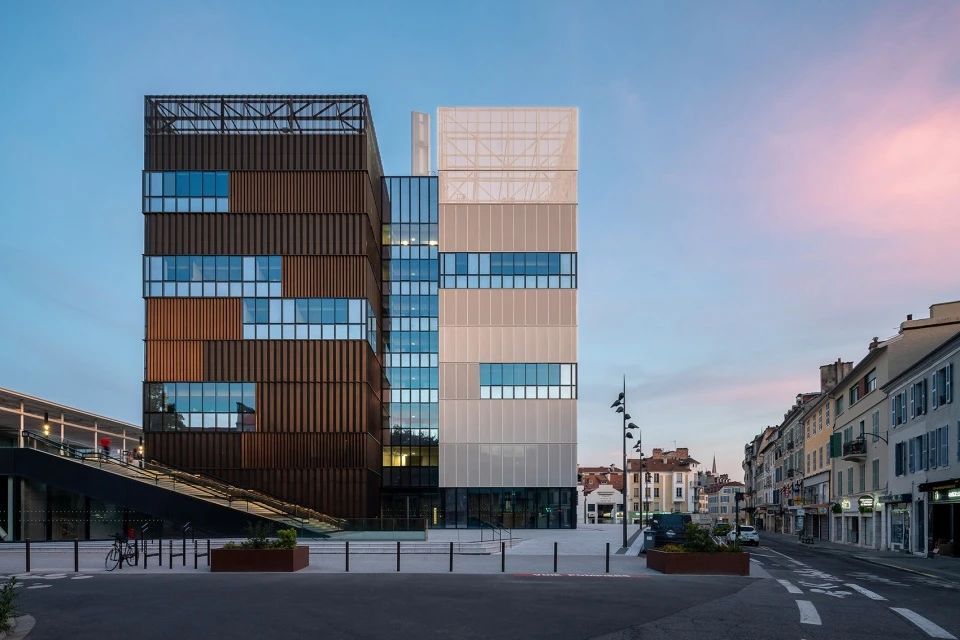
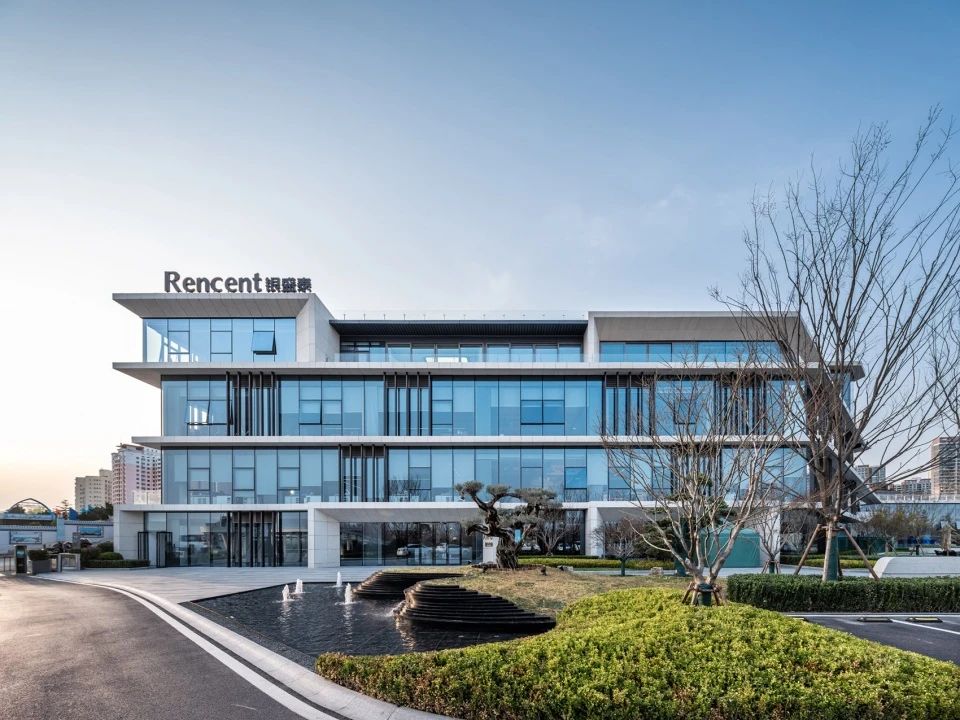
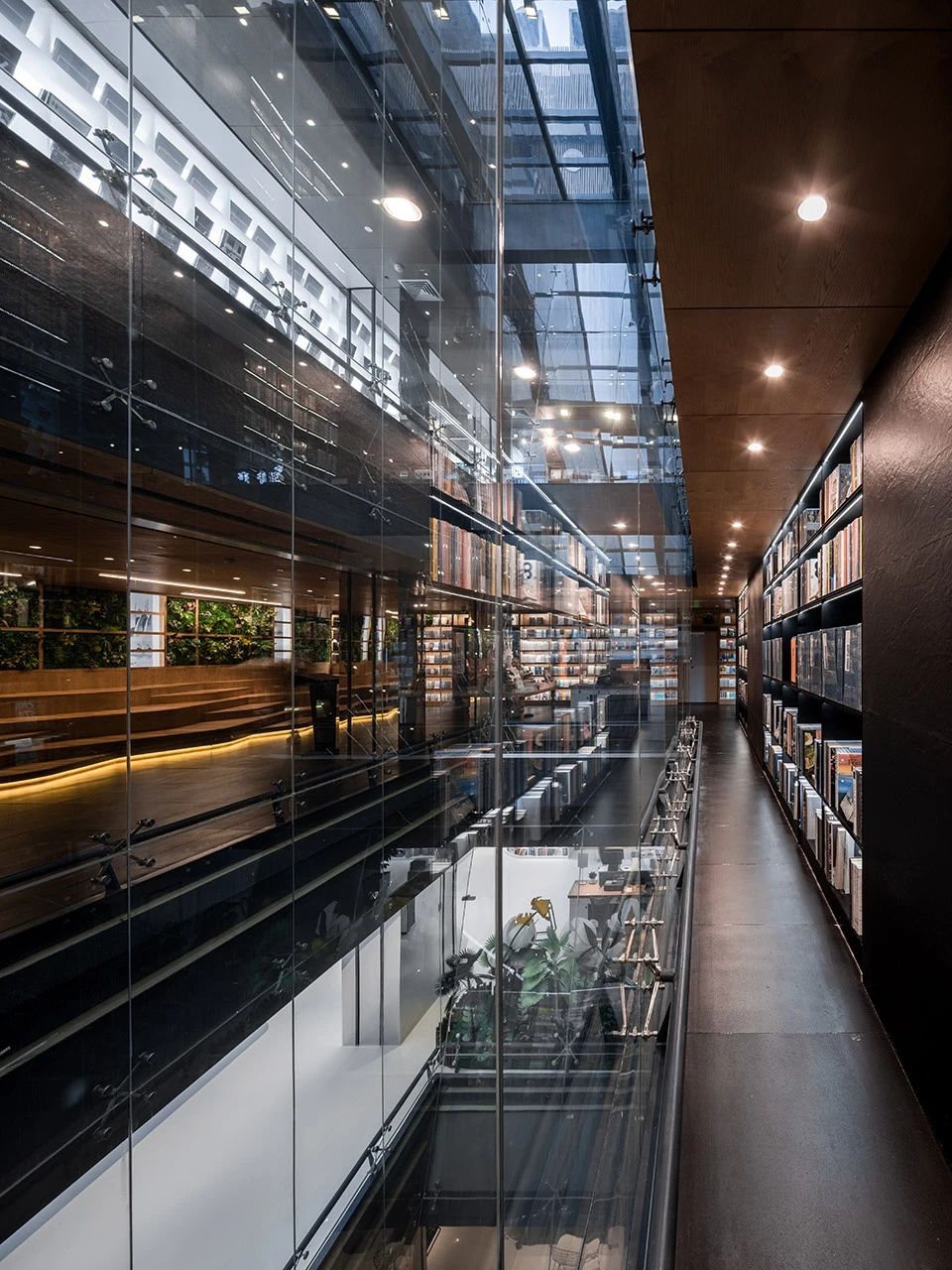
01.Material Summary

Float glass
It is a common flat glass and a widely used basic material in modern architecture, decoration, and industry. It is favored for its flat, transparent and smooth surface characteristics. Float glass is manufactured through a production process called float method.

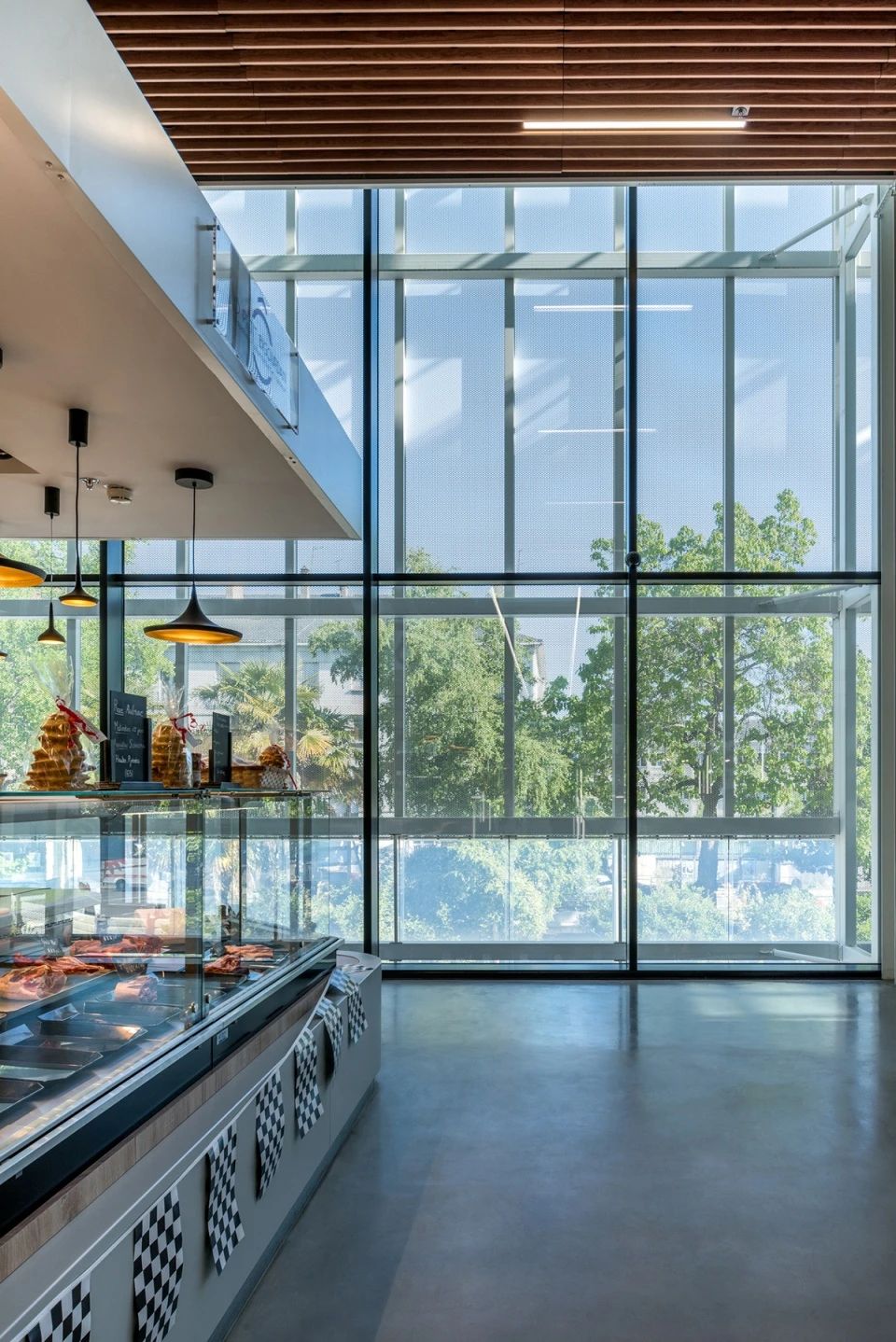
02.Material characteristics
1)Flatness
The surface of float glass is very flat, without obvious unevenness or bending. Fire resistance: Metal tiles have strong fire resistance, with a fire resistance rating of A level, will not burn, and also have a certain degree of flame retardant ability.
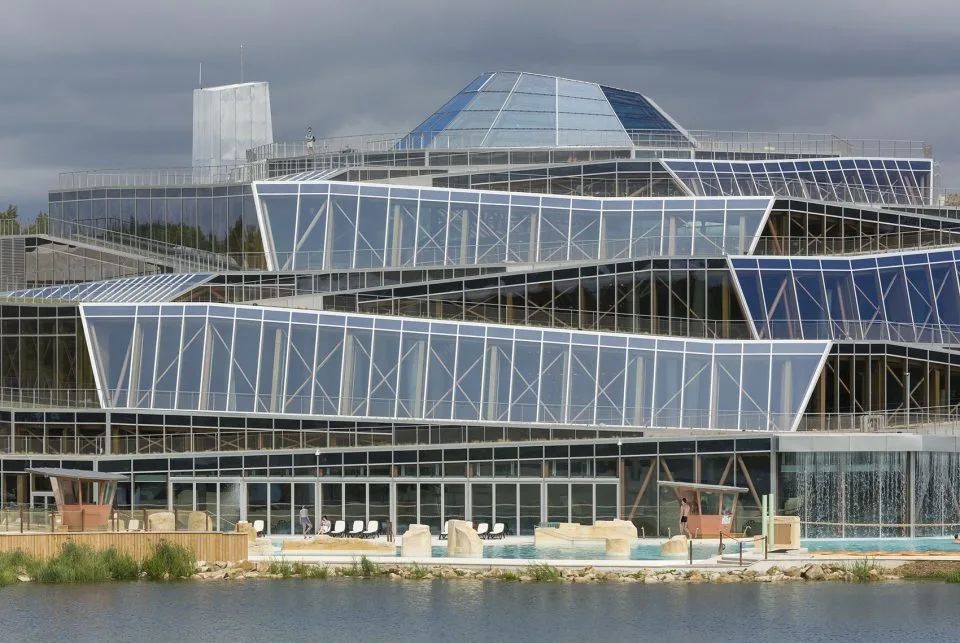

2)Transparency
Float glass has high transparency, allowing a large amount of light to pass through and ensuring indoor brightness.
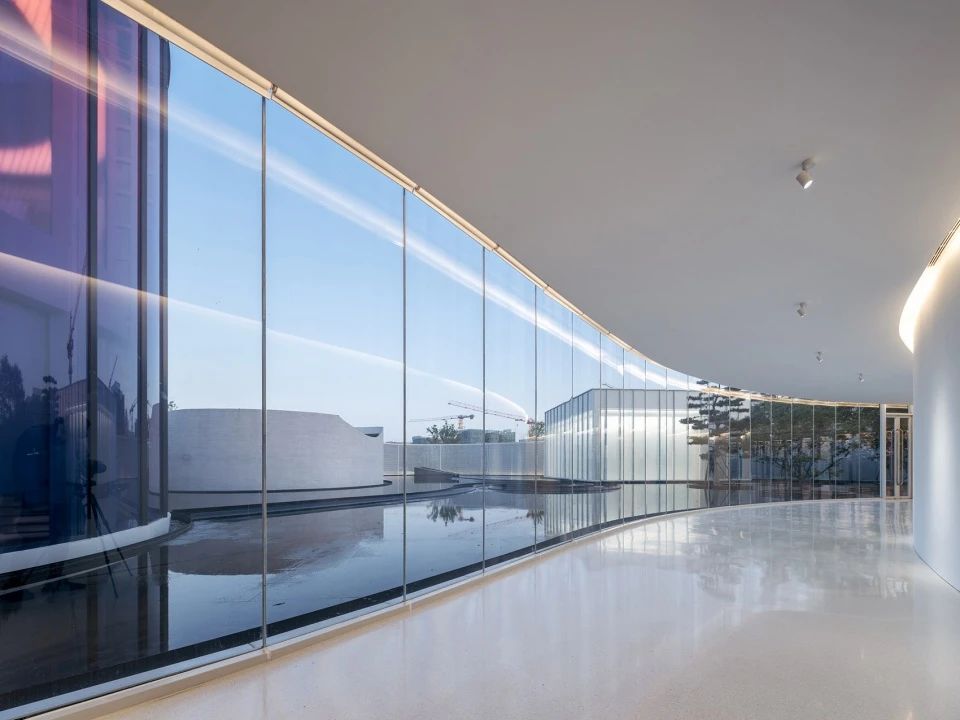

3)Smoothness
The surface of float glass is very smooth, without any roughness or obvious defects.
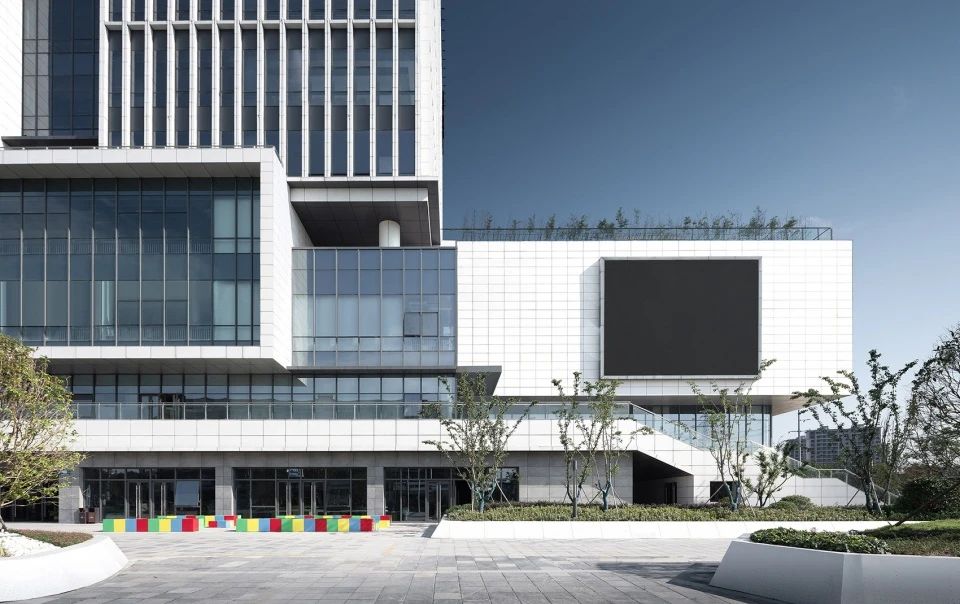

4)Widely applicable
Float glass is widely used in the fields of windows, doors, curtain walls, furniture, household appliances, mirrors, and decoration in buildings.
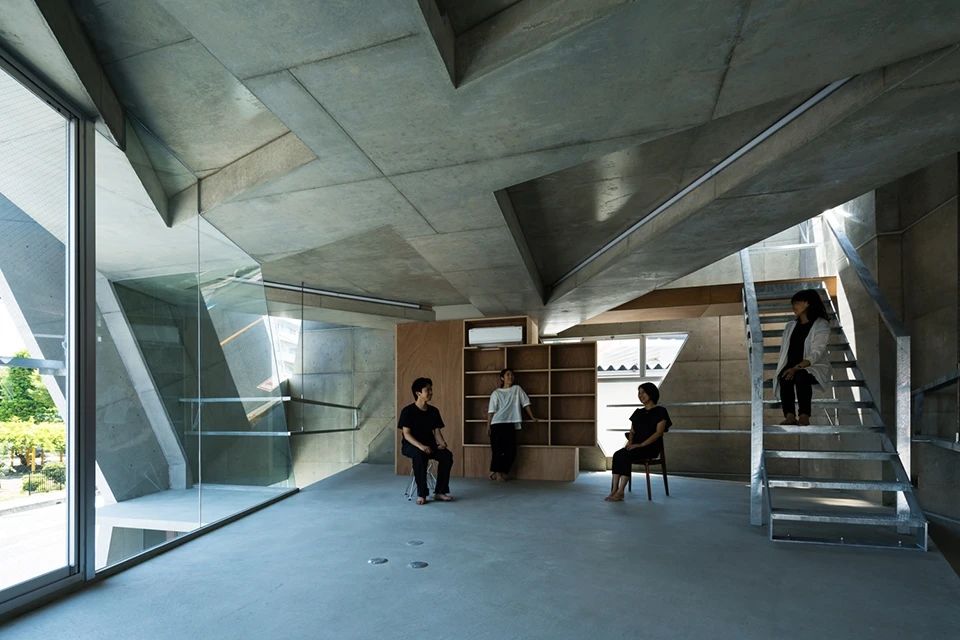

5)Processability
Float glass can be cut, ground, drilled, and processed to meet different applications and design requirements.

6)Stability
Due to the production process of float glass, its thickness is relatively uniform and less prone to deformation.

7)Quality
The manufacturing process of float glass gives it high quality, consistency, and predictability.

03.Material technology
The production process of float glass is the (float) method, which is the main method for manufacturing flat glass.
The specific production process of float glass:
1. Preparation of raw materials
Mix raw materials such as quartz sand (SiO2), sodium carbonate (Na2C03), limestone (CaCO3) in a certain proportion. These raw materials are heated at high temperatures and melted into glass liquid;
2. Float pool
Slowly pour the melted glass liquid into a huge float tank (also known as a float tank). The pool is filled with liquid tin metal, causing the glass liquid to float on the surface of the tin metal;
3. Formation and cooling
The glass liquid spreads evenly on the surface of the tin metal, forming a flat glass strip. As the glass cools on the tin metal, it gradually solidifies;
4. Curing and cutting
Glass gradually solidifies during the cooling process and is then cut into the required size;

5. Quenching
Some float glass will be sent to the quenching furnace Q for rapid cooling to increase its strength, making it a safety glass.
6. Inspection and quality control
After cutting and quenching treatment, the glass needs to undergo strict inspection to ensure that it meets the standard requirements in terms of size, flatness, transparency, etc;
7. Packaging and transportation
After passing the quality inspection, the glass will be packaged and transported to customers or sales points.
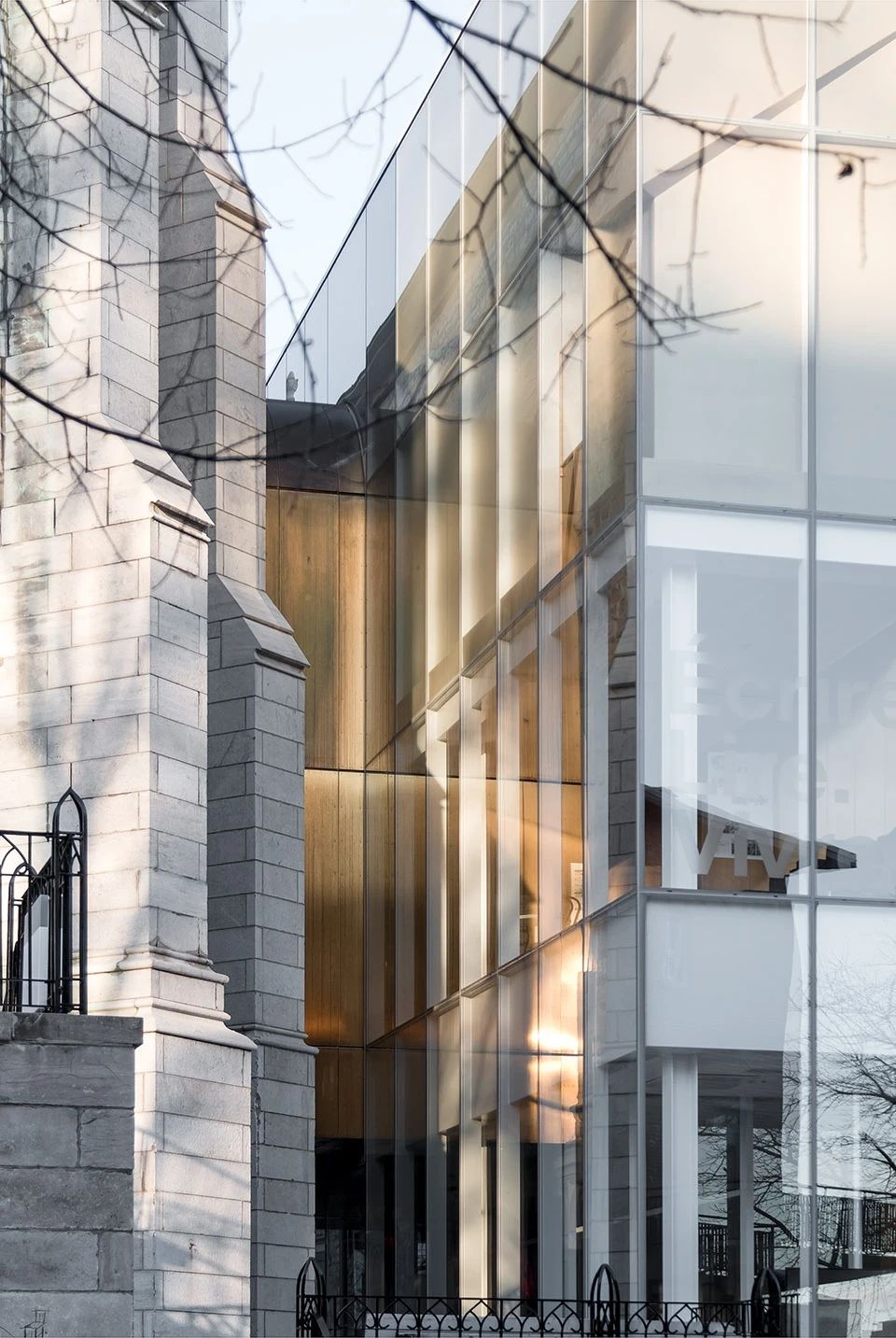
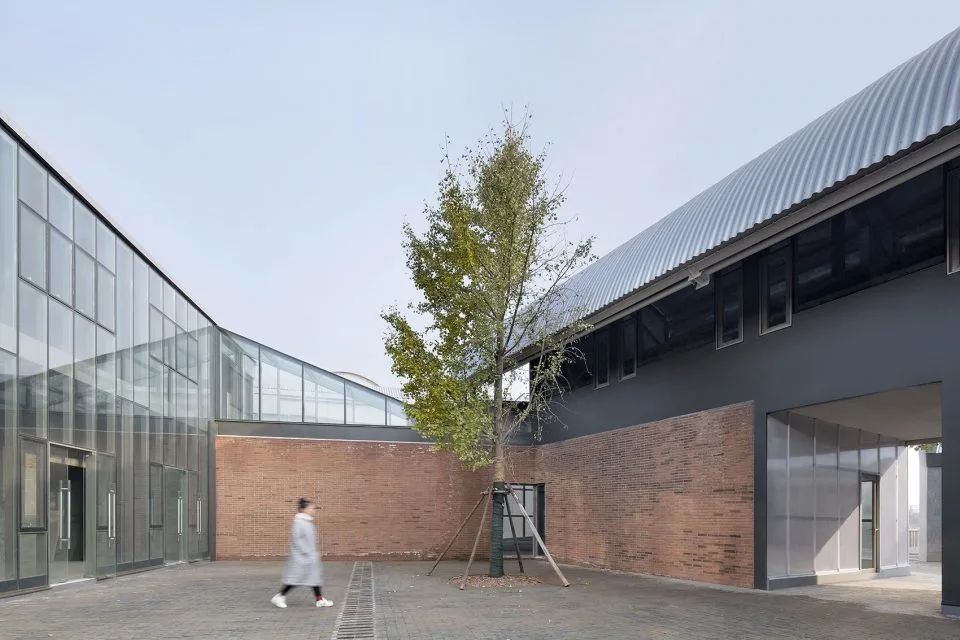
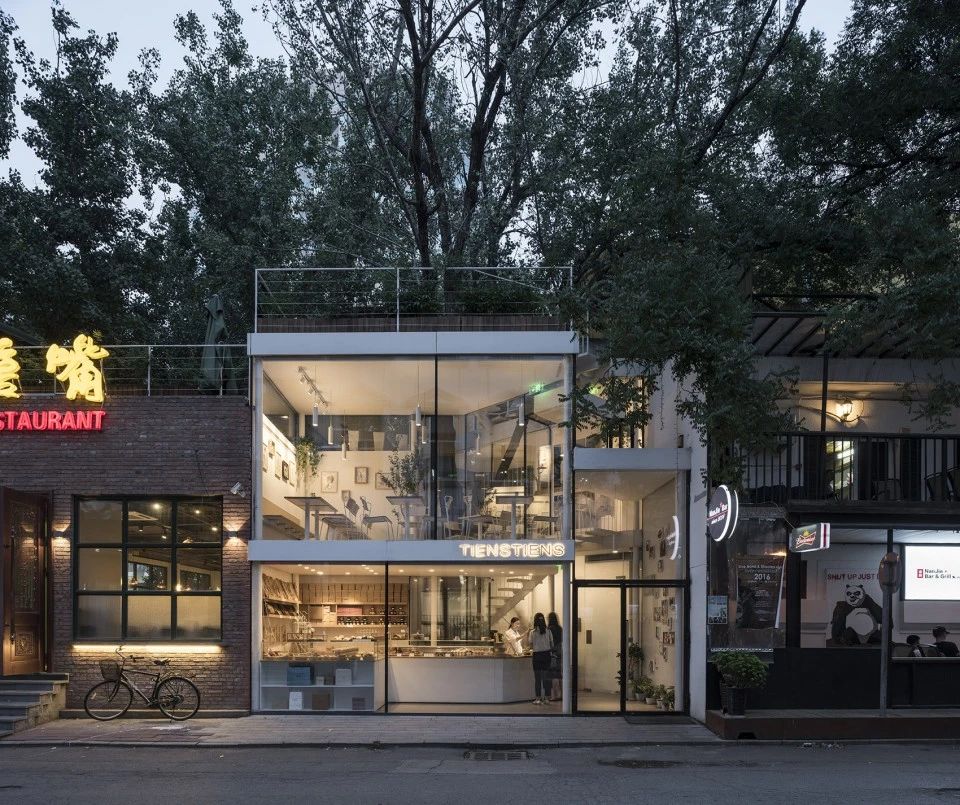



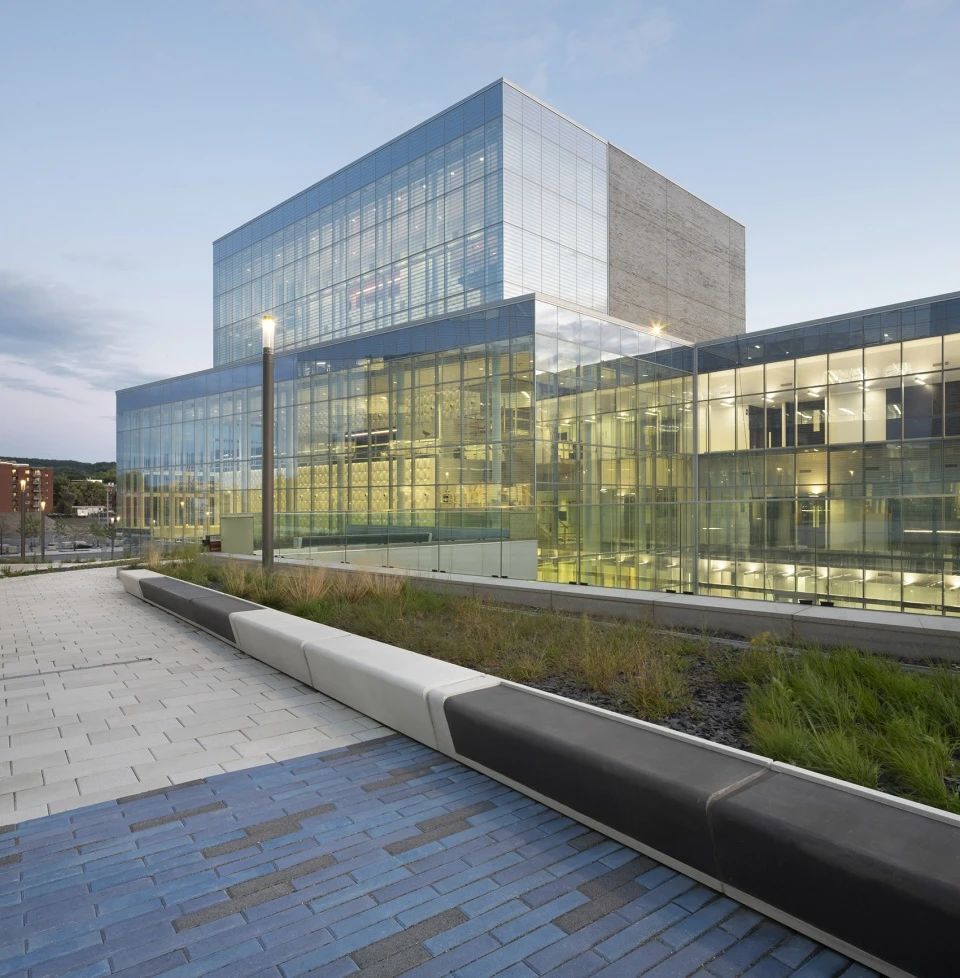
04.Classic Cases
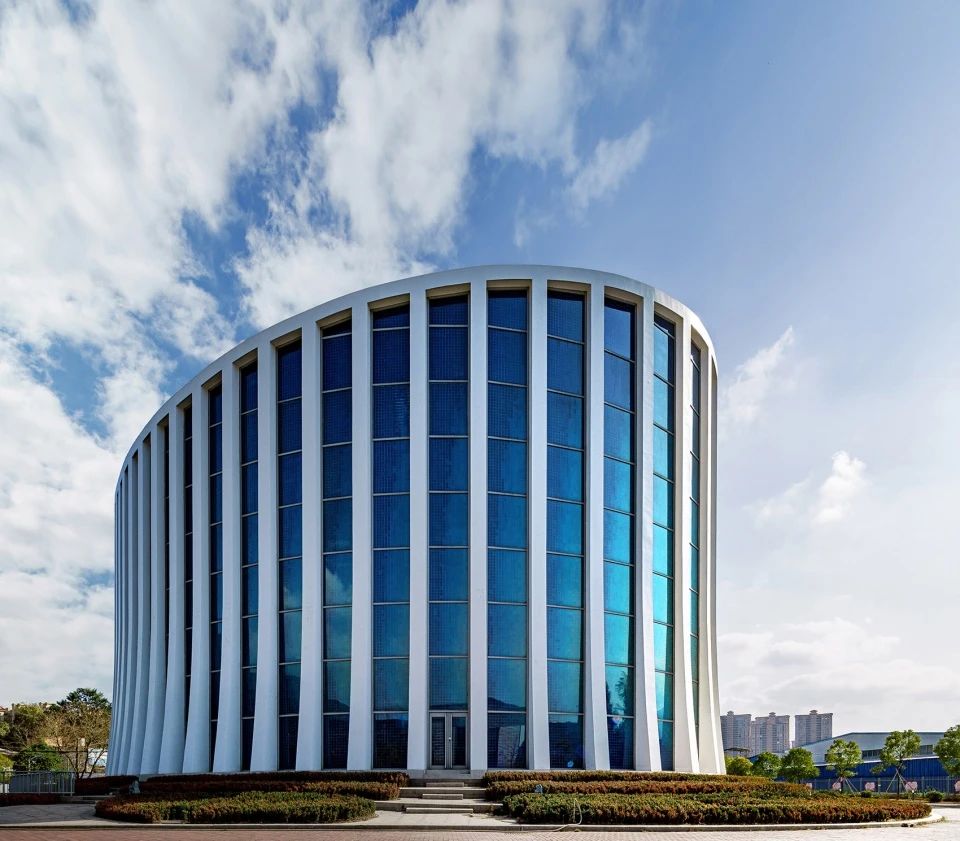
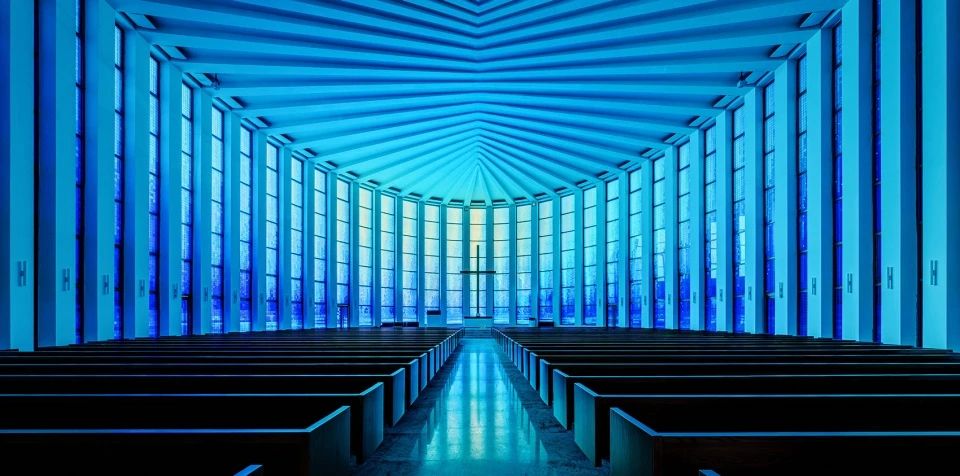
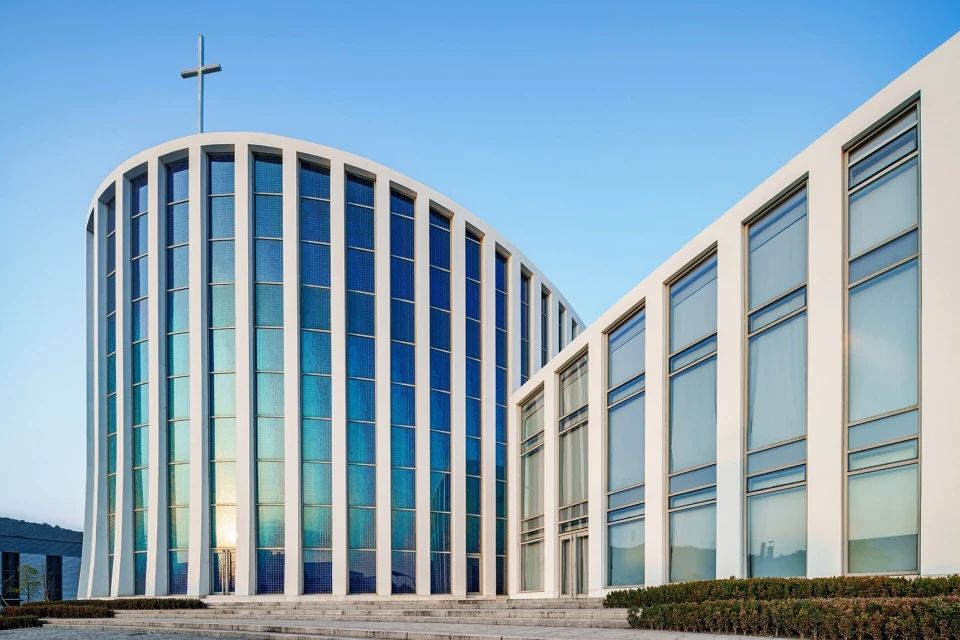
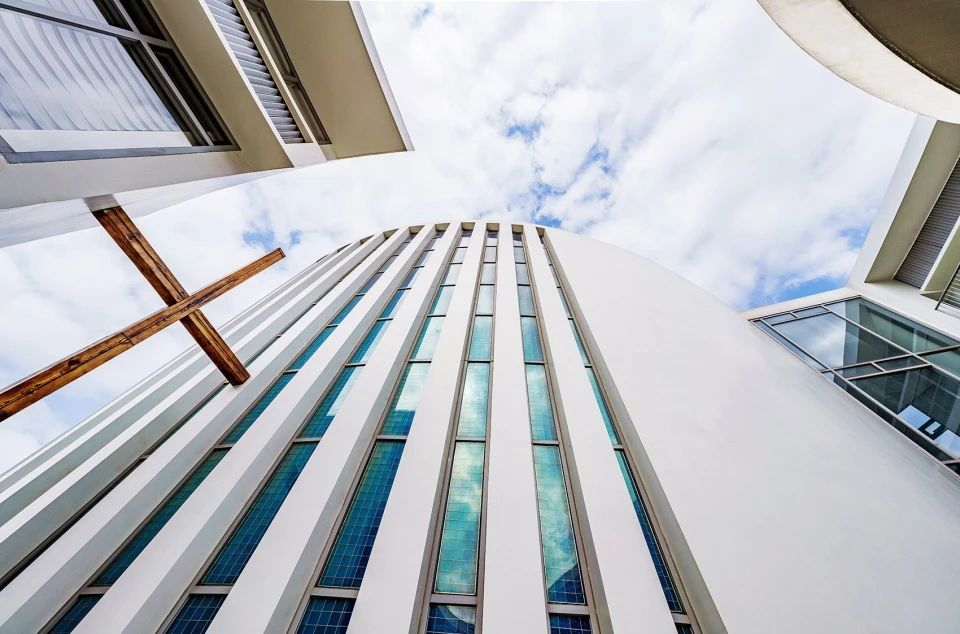
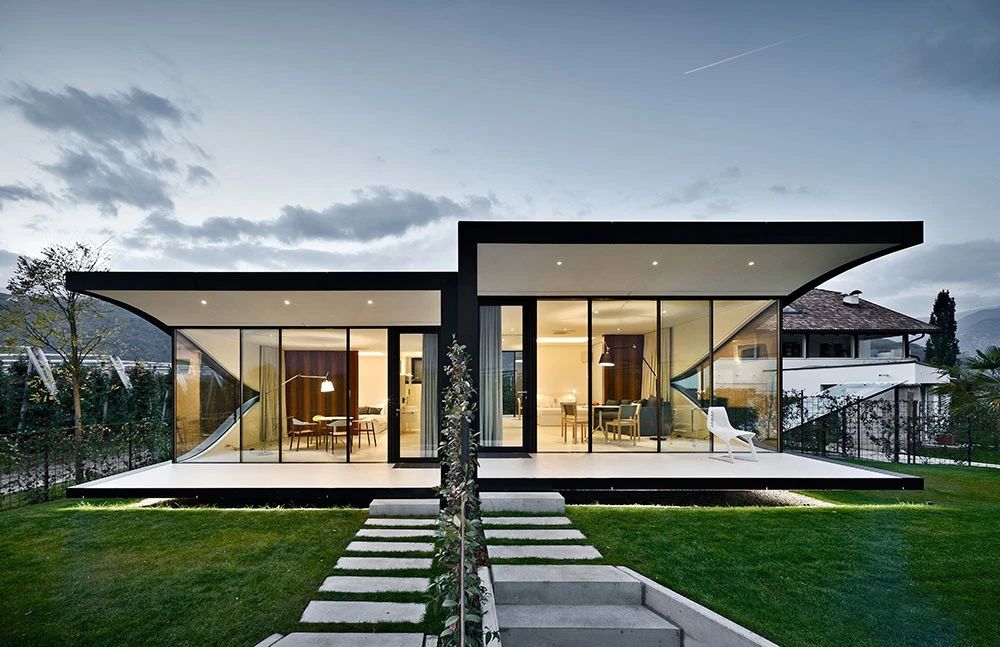
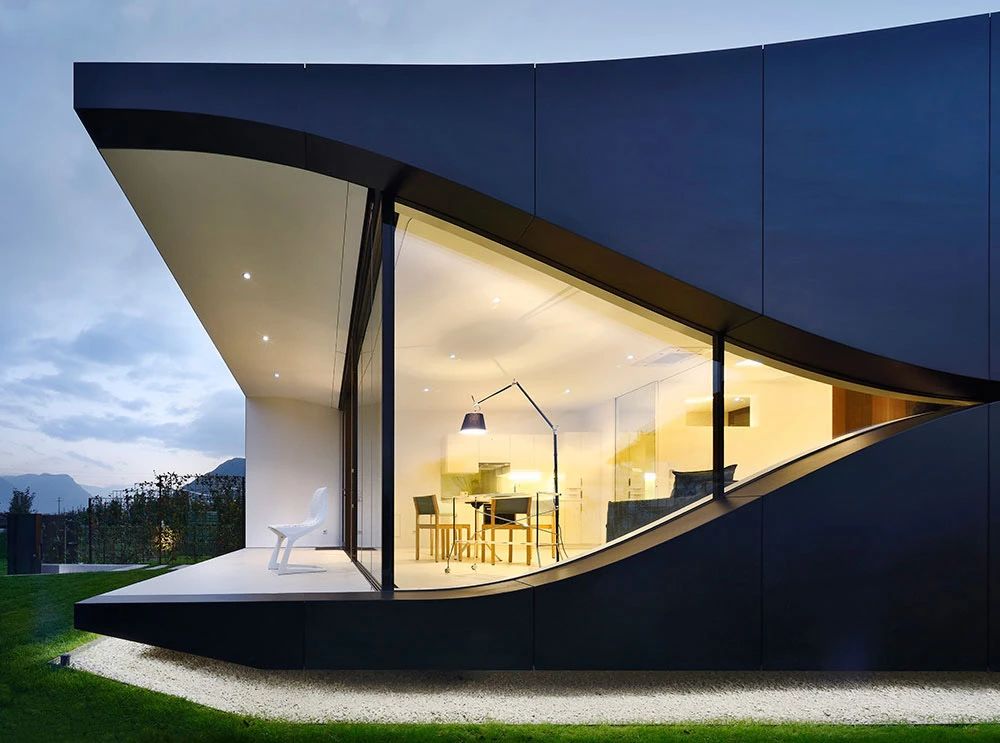
01.Luoyuan Binhai Hall, Fujian/INUCE. Dirk U. Moench
The belief lighthouse in the suburbs of Jiali City
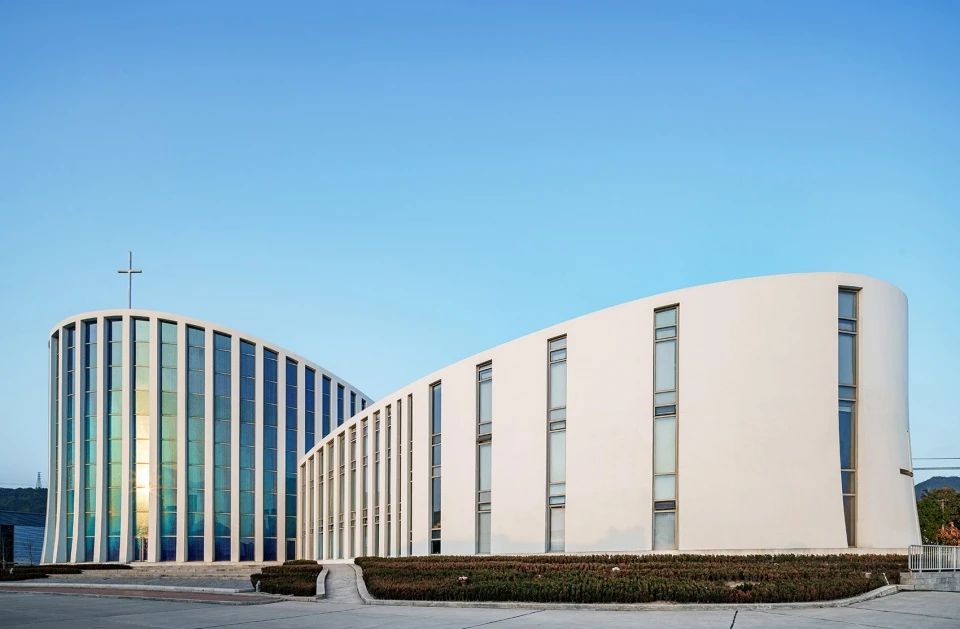
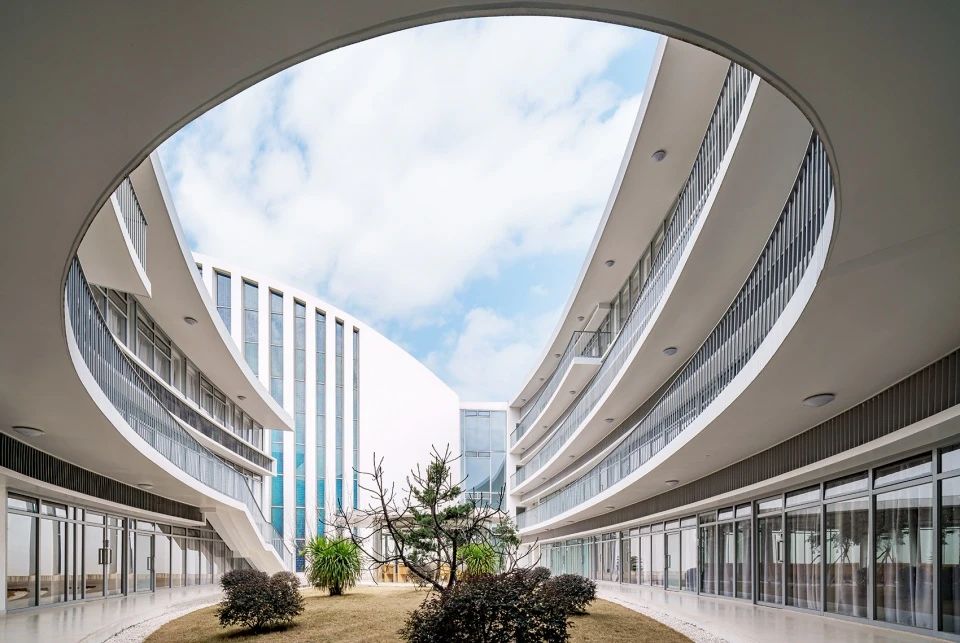
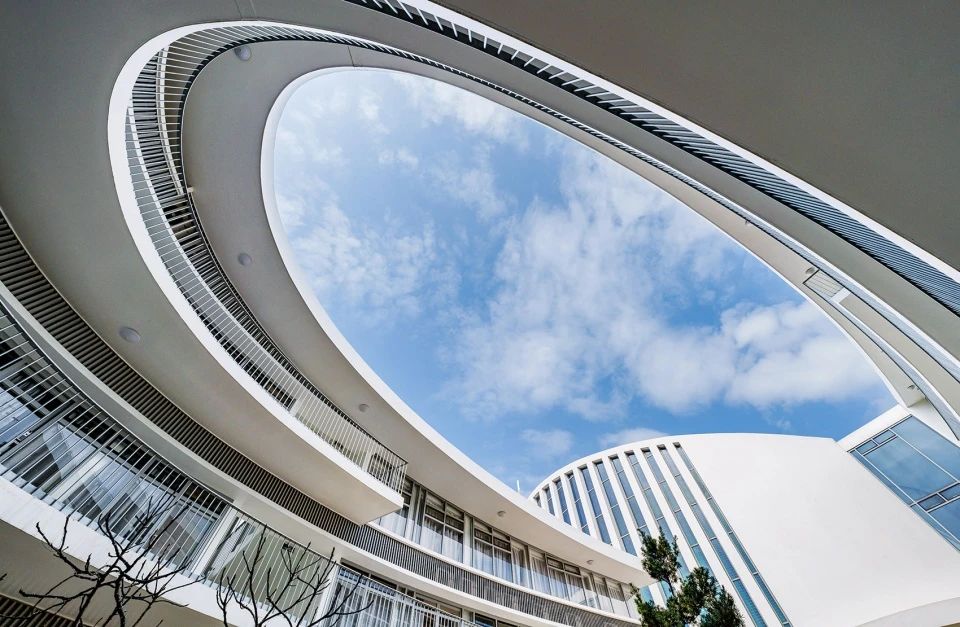
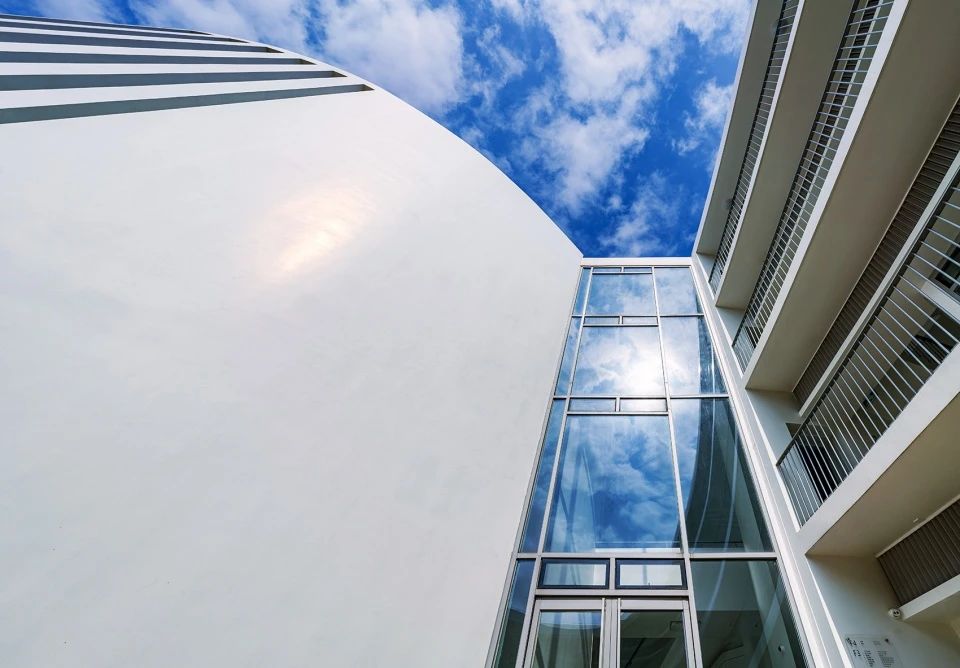
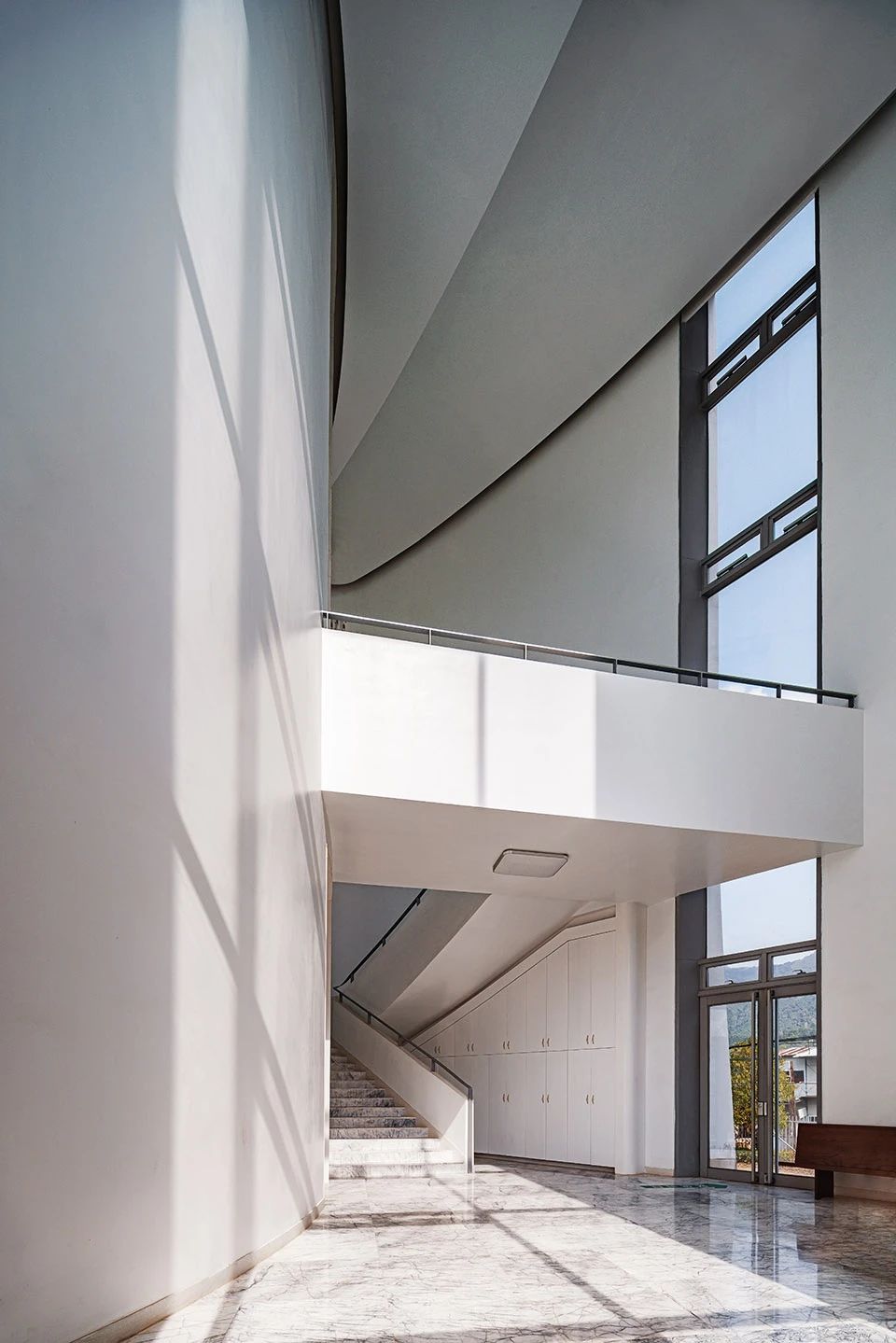
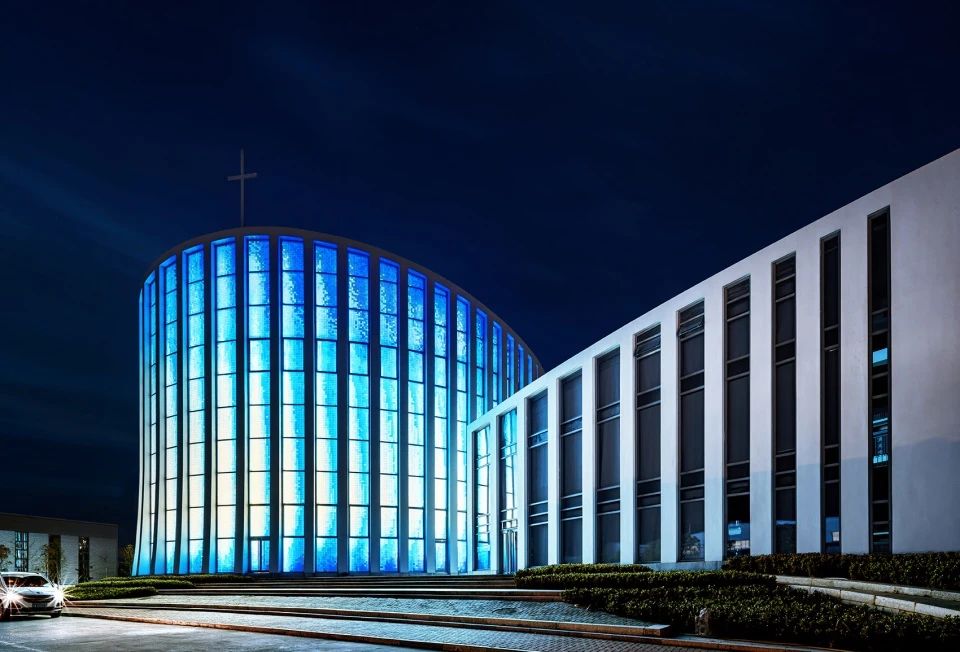










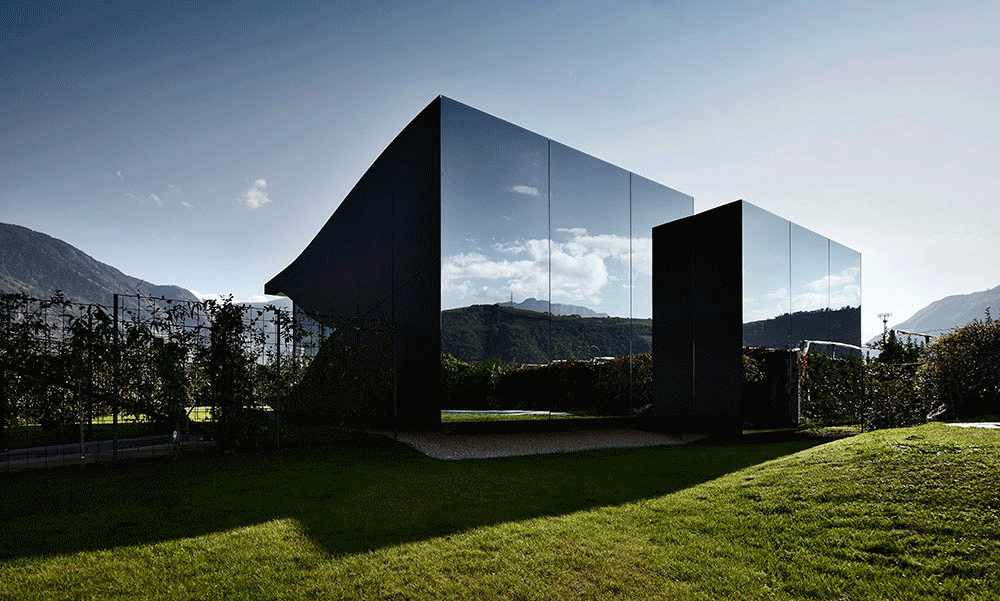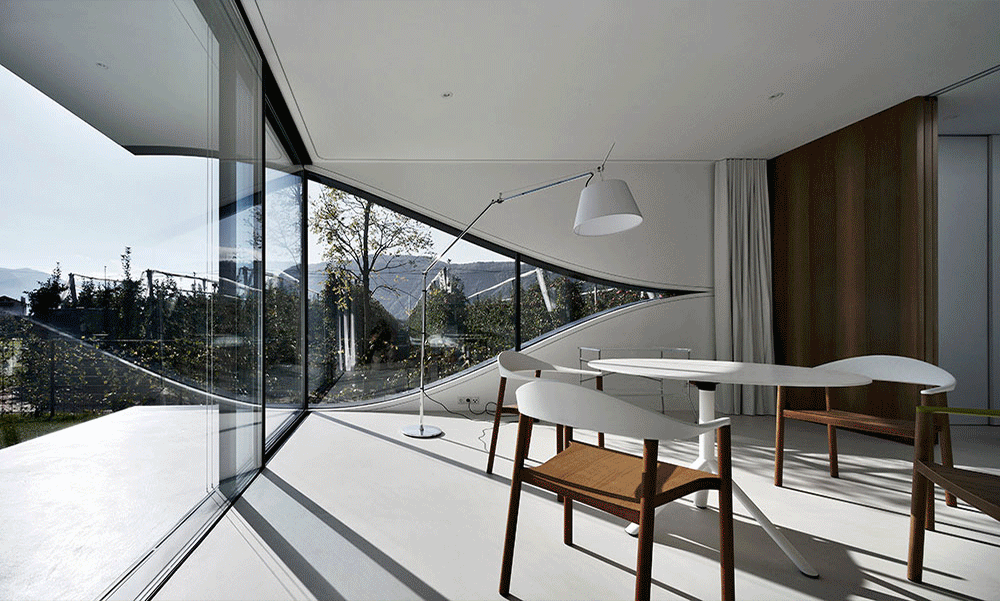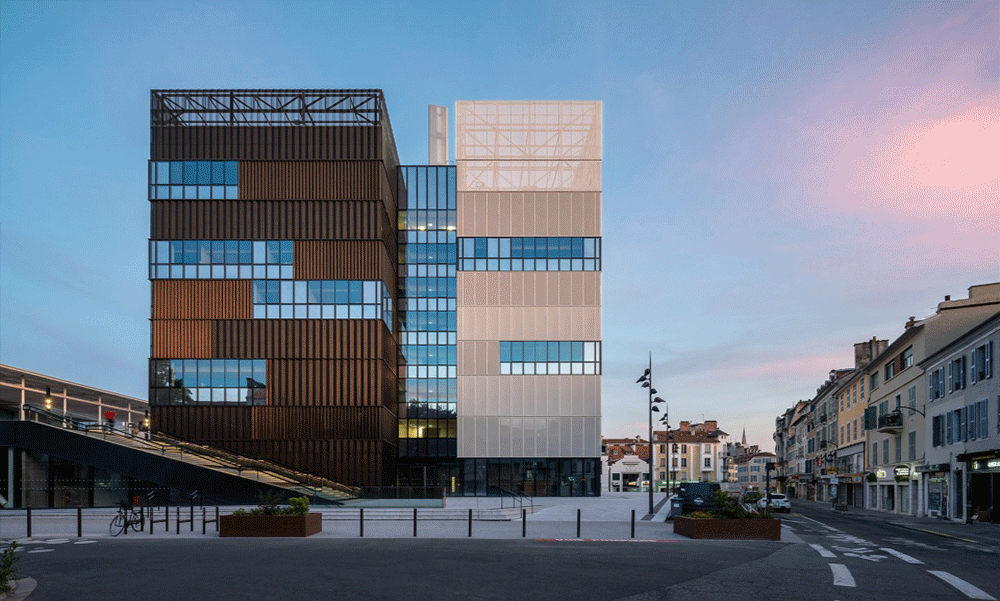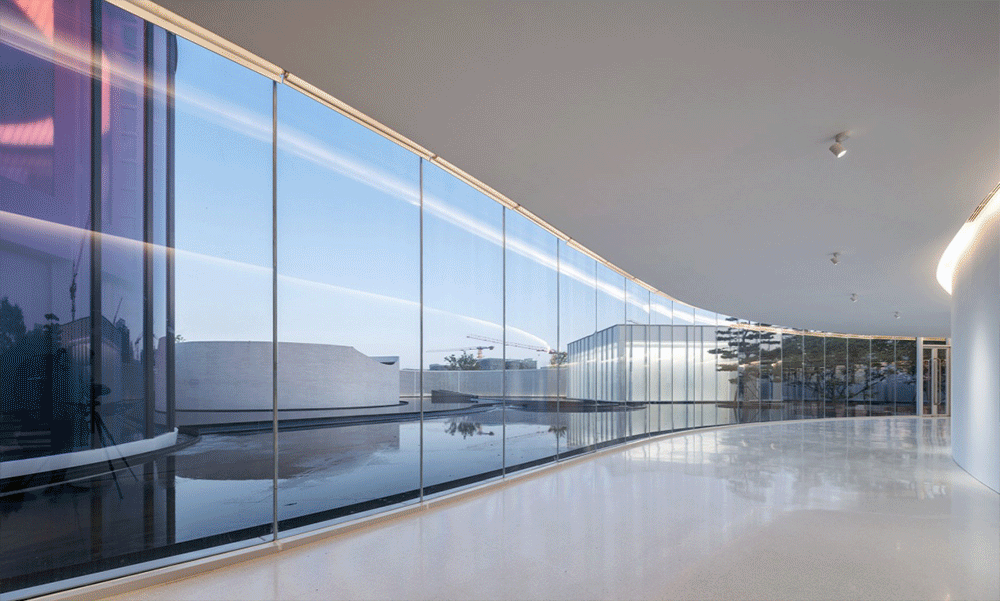
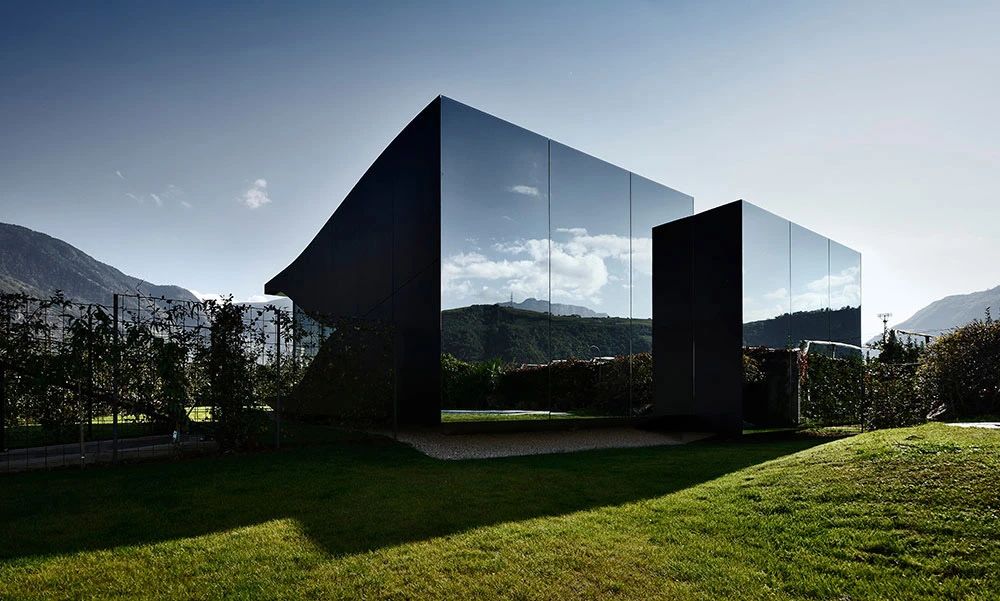
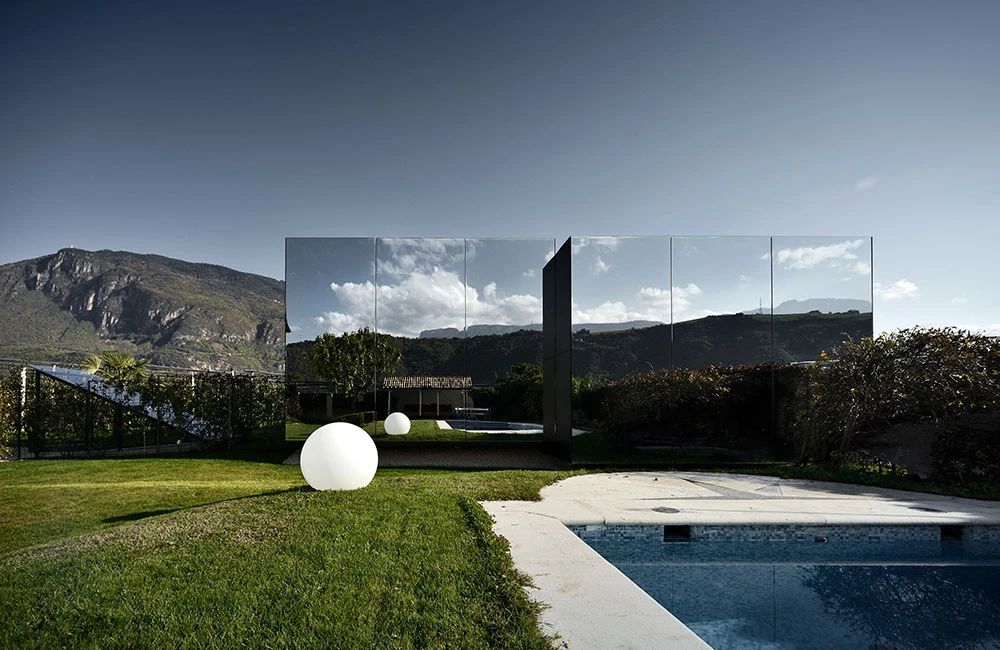
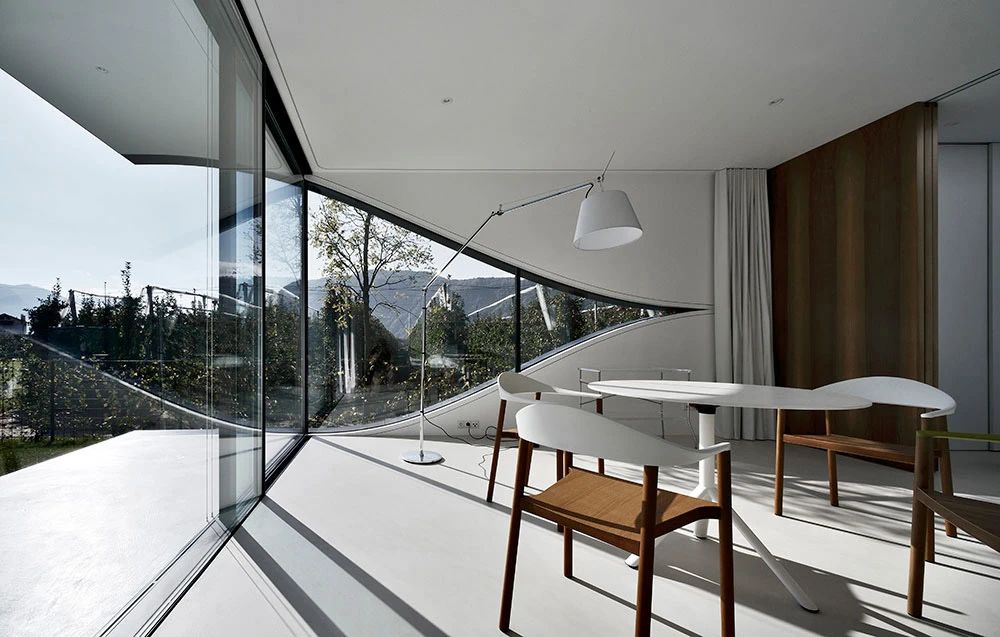
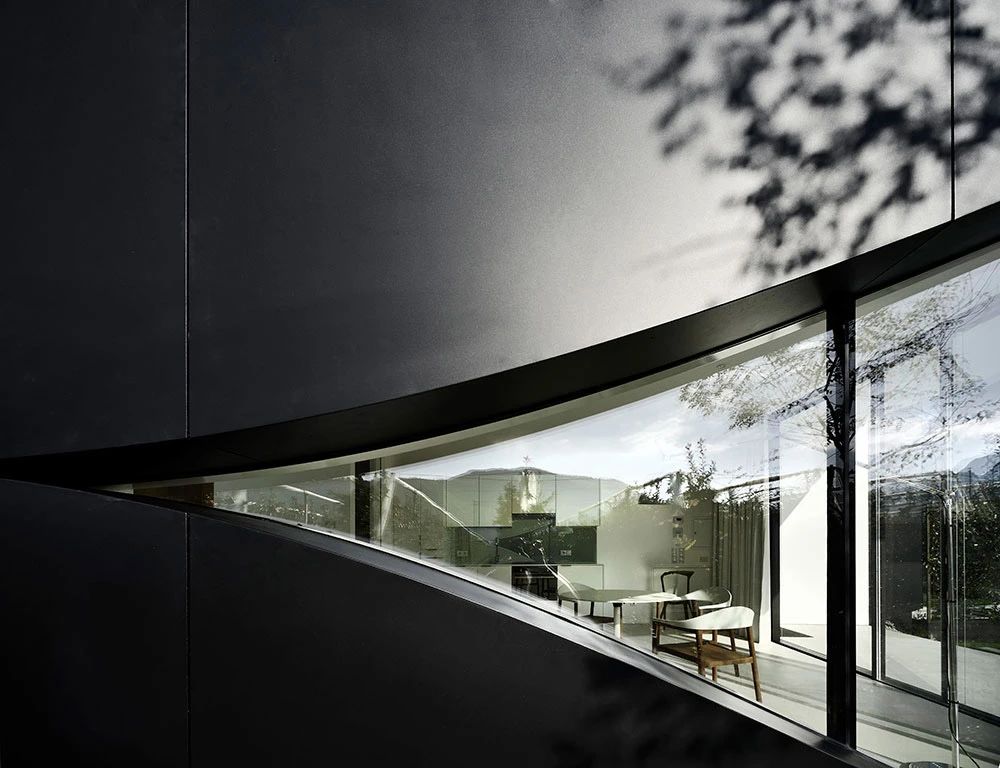
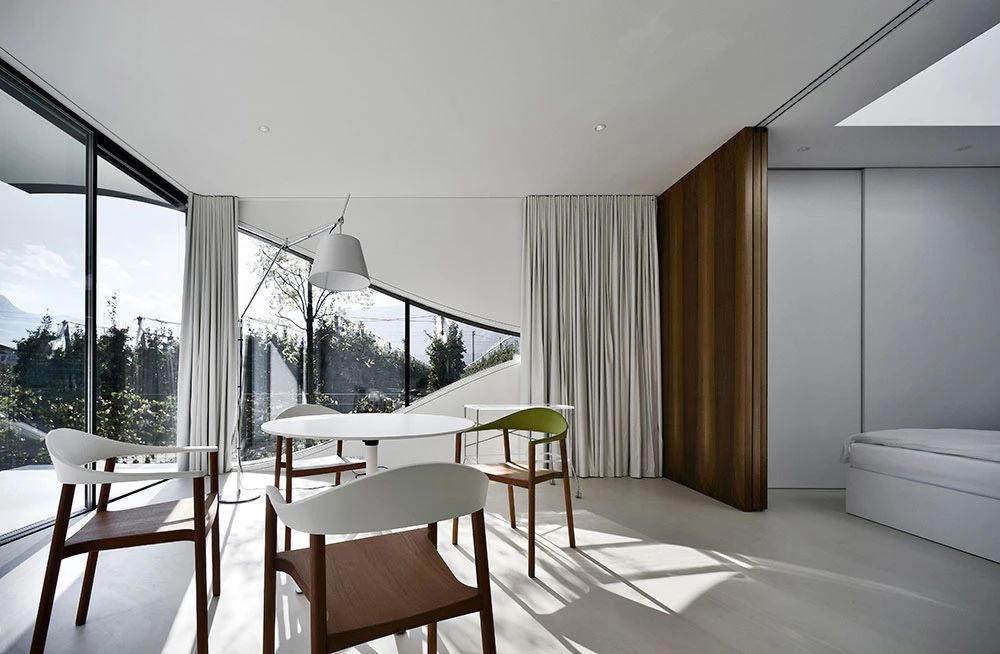
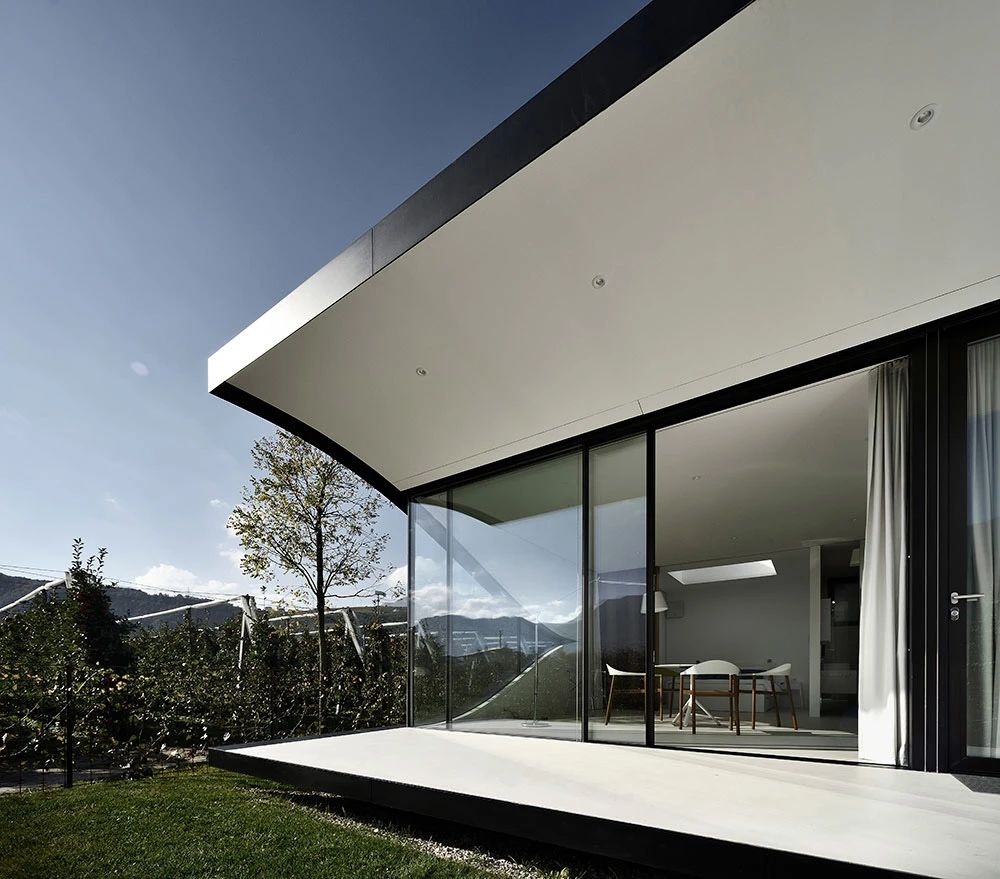
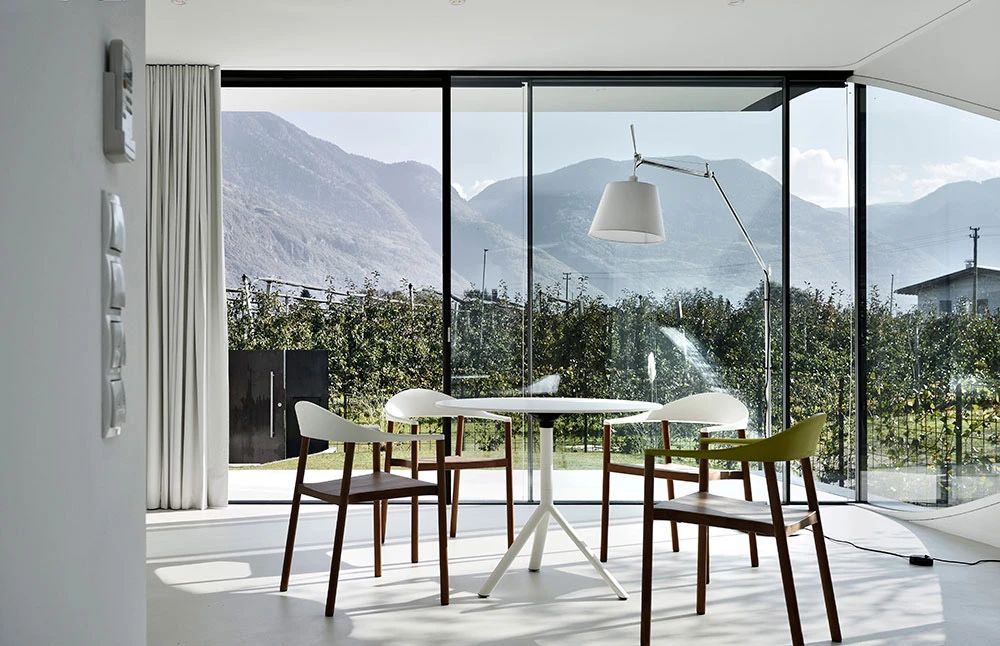
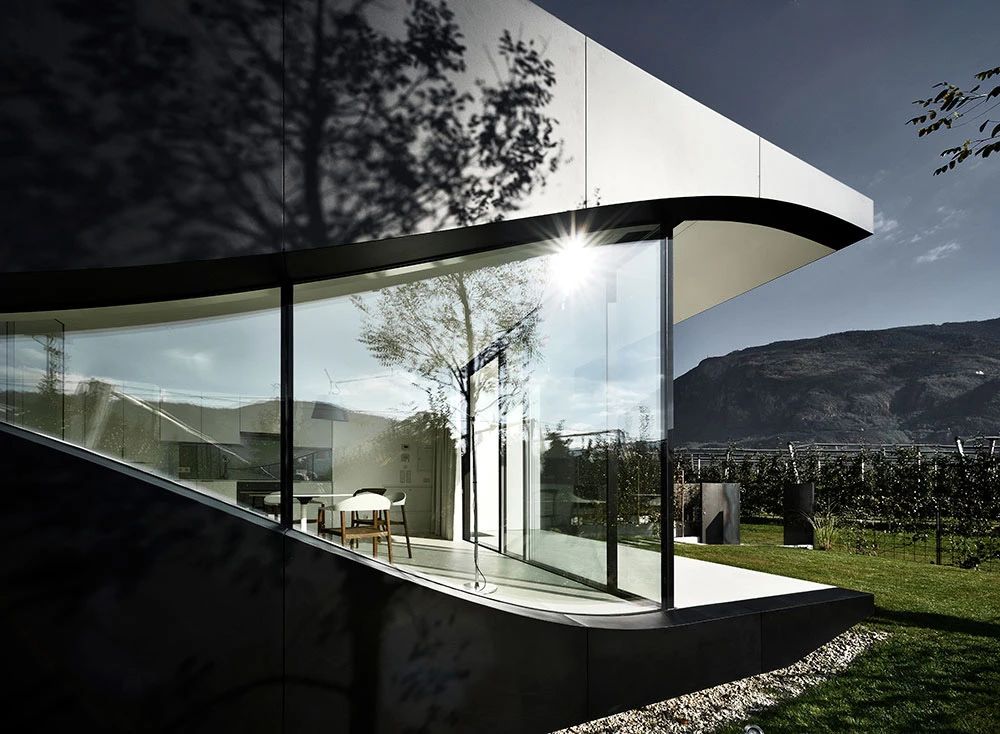
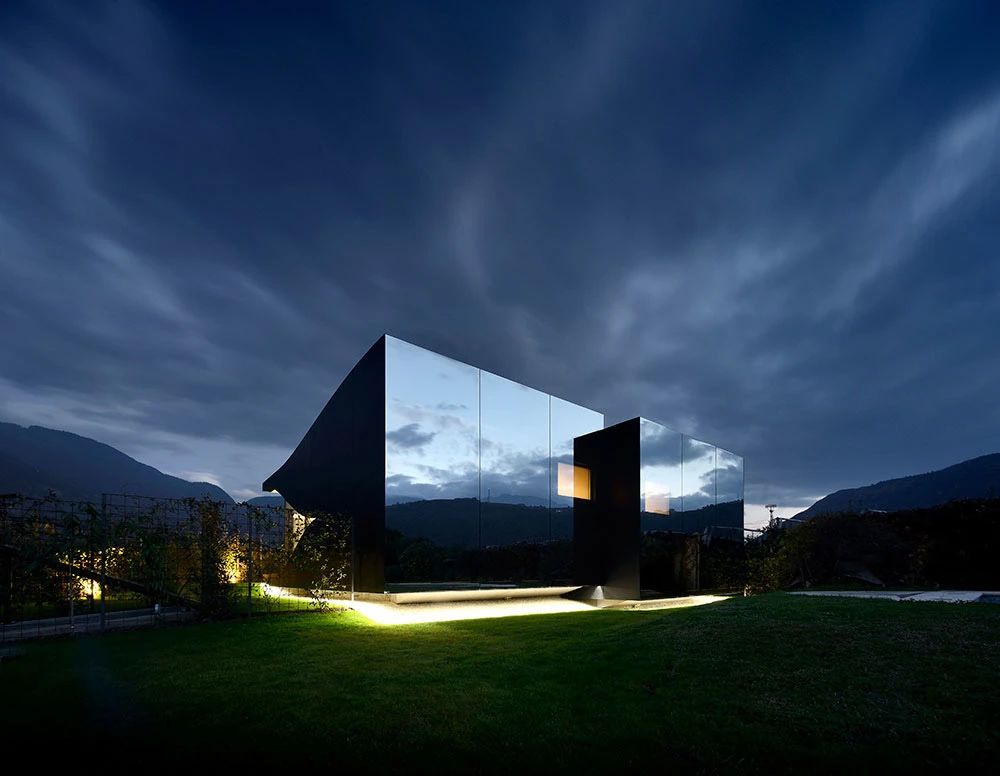
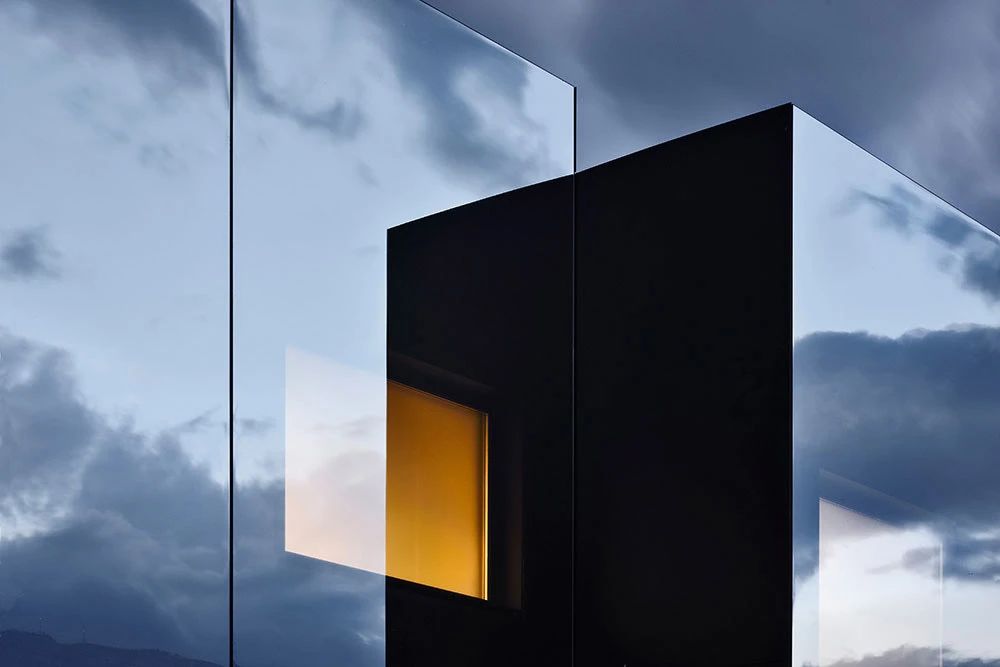
02.Mirror Vacation House, Italy/Peter Pichler Architecture
Modern architecture that blends with nature













The article is from Weixin Design