
With the development of Glass production and deep processing technology, the application of glass in architecture has risen to a new height. The use of glass has also expanded from early windows and curtain walls primarily aimed at lighting and ventilation to interior and exterior wall decorations, roofs, floors, and even become structural materials. Glass has also evolved from a pure functional material that pursues transparency and visibility to an omnipotent interior and exterior decorative material. Today, the great genius will share what are the common glass processing techniques in architecture?

01.Coated glass
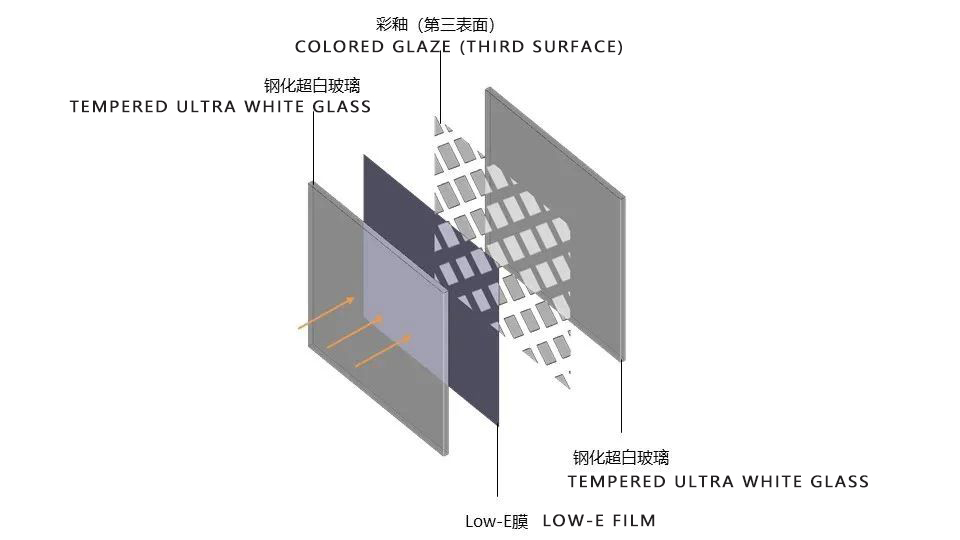
Glass coating is a process of coating one or more layers of metal, non-metal, alloy or metal compound films on the surface of glass, including heat reflective glass and Low emissivity (LOW-E).
Its function is to isolate heat and ultraviolet rays, with good energy-saving effect, and to enhance the reflectivity of the glass hardness coating surface, which can generally reach 20-40%.
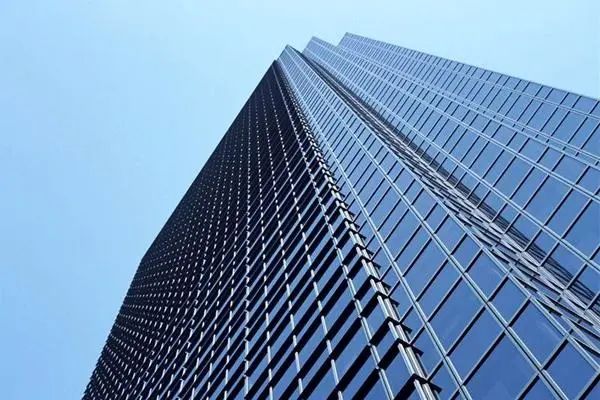

The dimensions of conventional coated glass panels often include:
2440x3660mm
2440x3300mm
2100x3300mm
It is said that the maximum size of coated glass in China can reach 3300x116000mm.
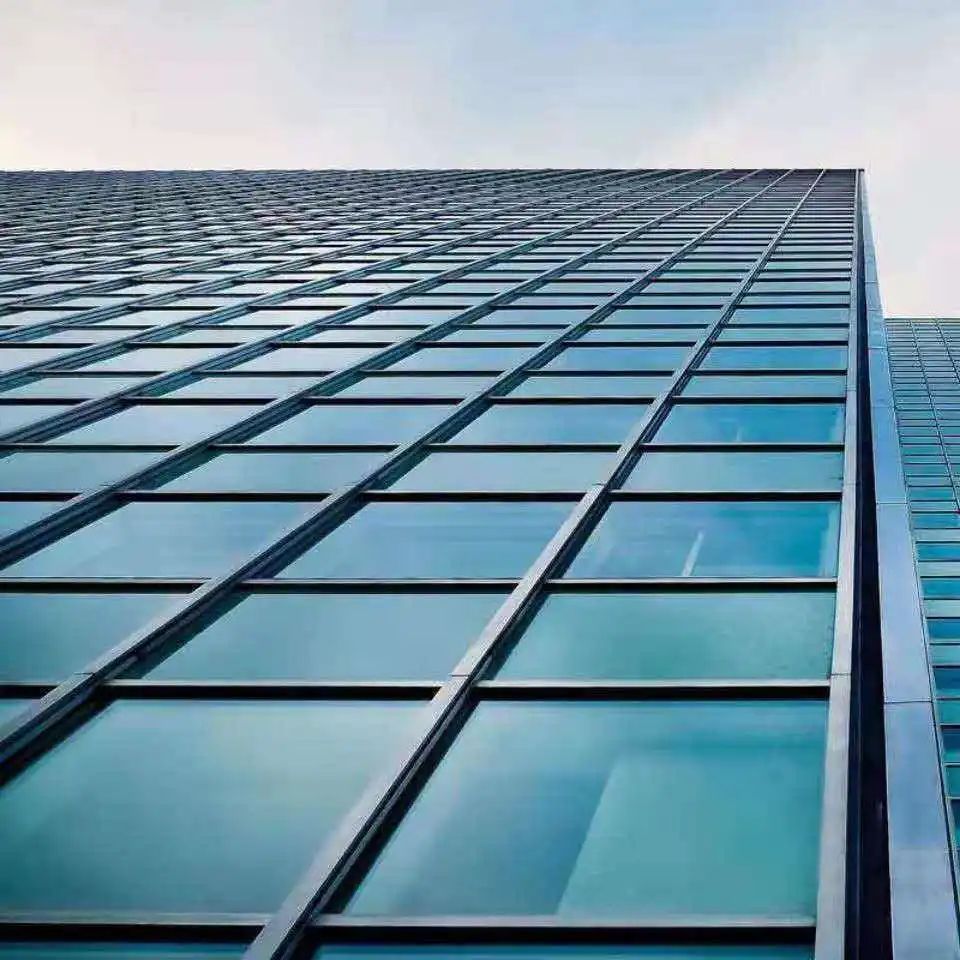

Coated glass can also choose "color". The color of coated glass is not the fixed color of the glass, but the spectral reflection color of the film layer, so theoretically it can reflect light of different wavelengths, including any color in visible light.
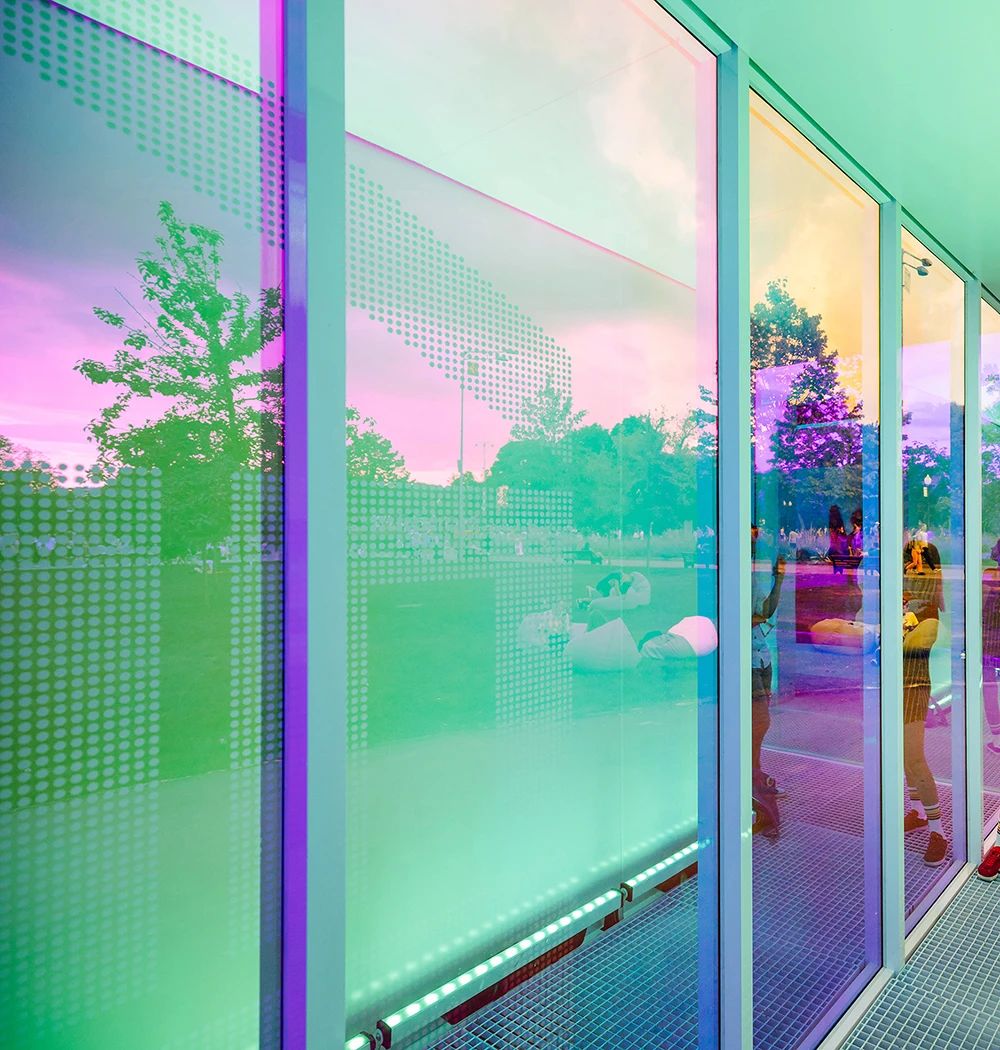

▲Colorful coated glass
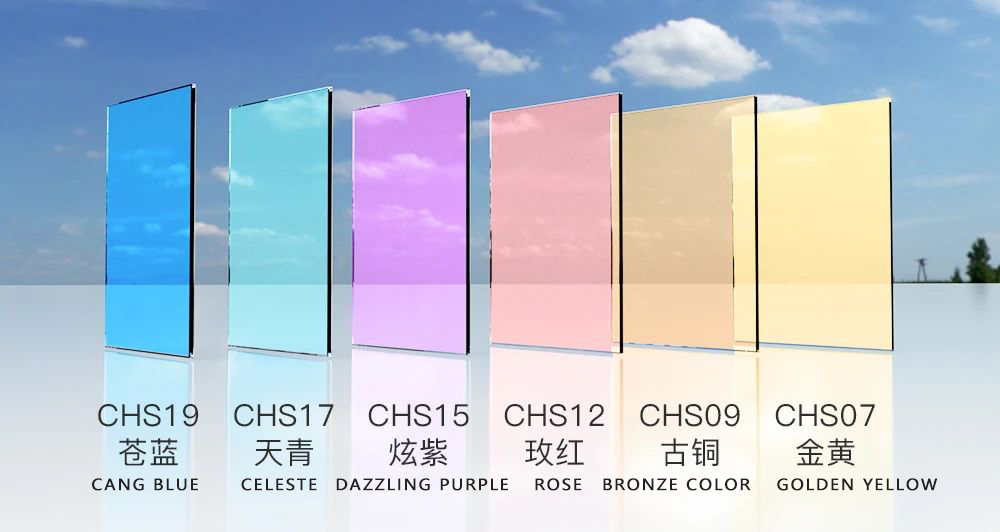

▲Colorful coated glass
Related Cases
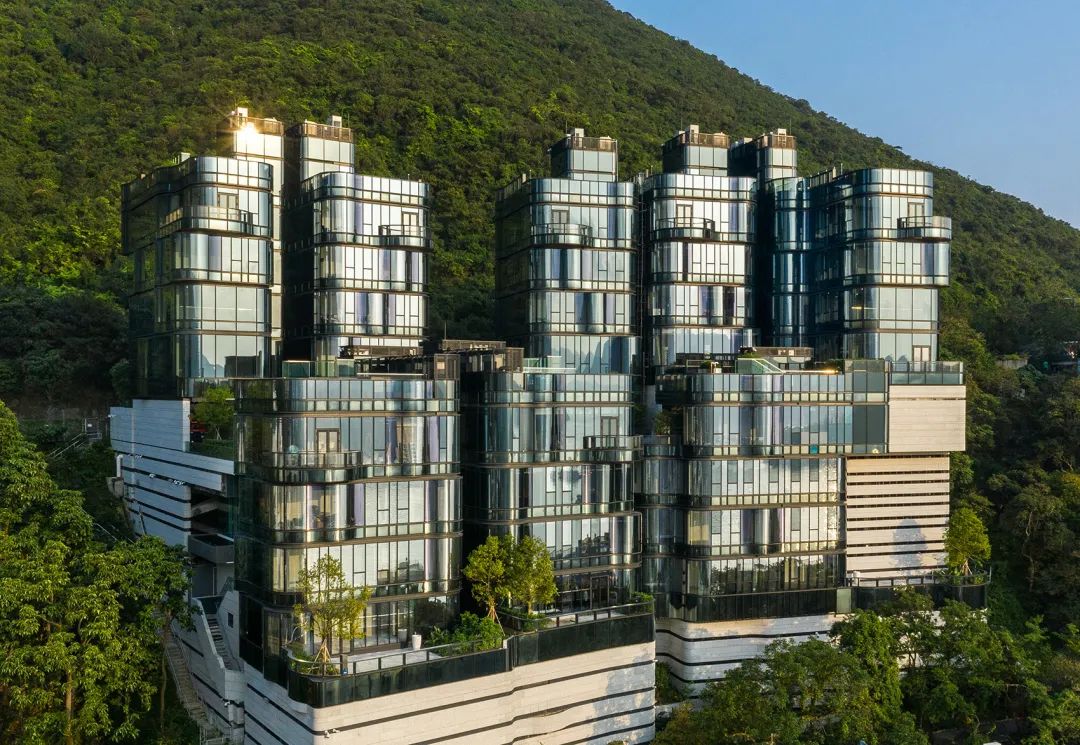
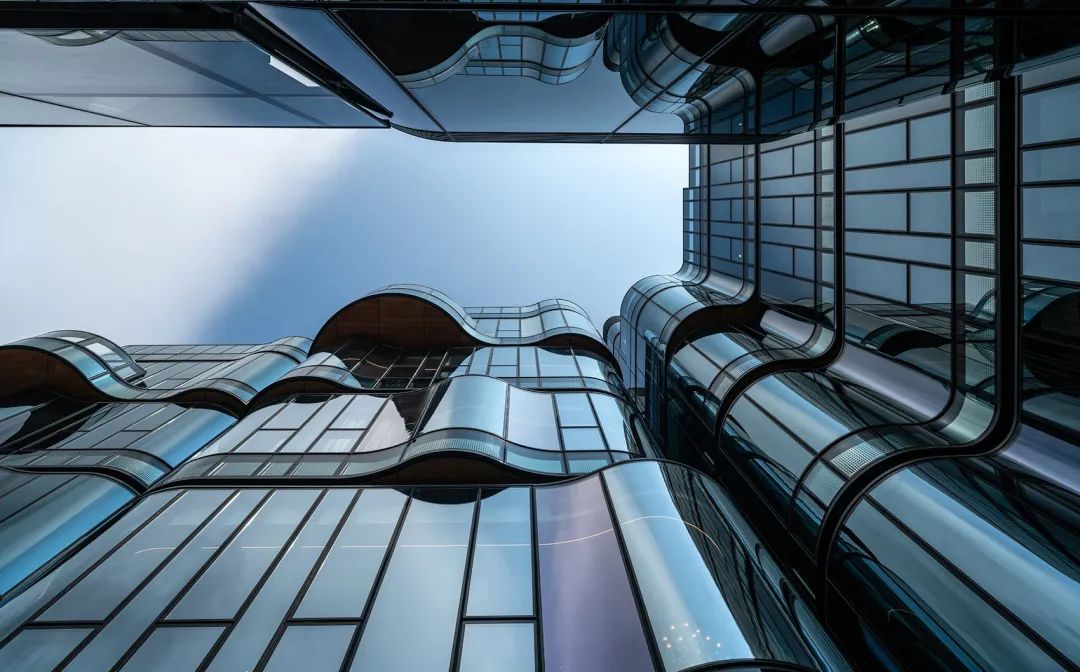
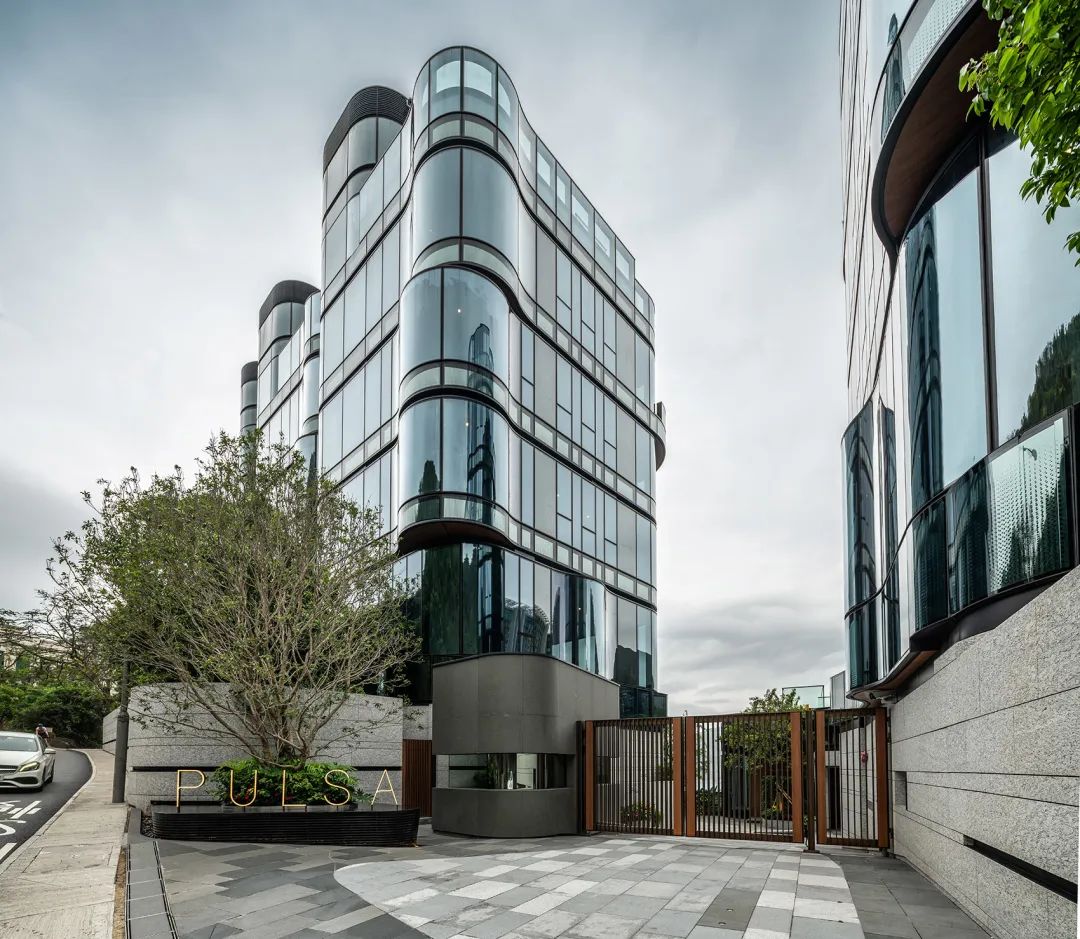
Repulse Bay PULSA/AEDAS
Using hollow LOW-E coated glass as the exterior facade. The use of convection windows, as well as the installation of rooftop swimming pools, elevated platforms, and comprehensive sun shading and insulation, enhance energy efficiency. The residential area has received a green building environmental impact assessment (BEAM) gold rating review.




02.Laminated glass
Laminated glass, or laminated glass, is a composite glass product that is permanently bonded by two or more pieces of glass through organic bonding materials.
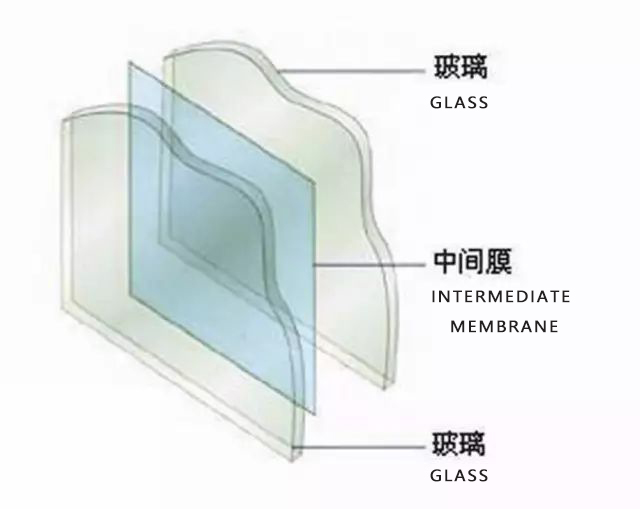
At first, Laminated glass was designed to keep clean and smooth when the glass was damaged by external force, and the glass fragments would not scatter to cause safety hazards.
There are many kinds of films in the middle of Laminated glass, such as colored films, which can meet different functional and decorative needs.
Common glass elements include Float glass, tempered glass colored glass, heat absorbing glass or heat reflecting glass. Common intermediate membranes include PVB, SGP, EVA, PU, etc.
In addition, there are some special intermediate membranes and interlayer materials. For example, color intermediate film, printing intermediate film, LOW-E intermediate film. Interlayer materials include paper, cloth, plants, silk, silk, and metal wire.
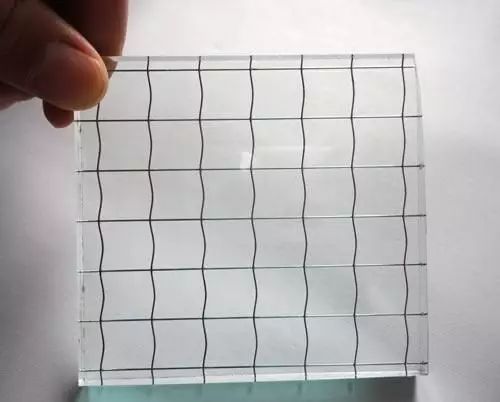
▲Wire Laminated glass

▲Printing intermediate film Laminated glass
Related Cases
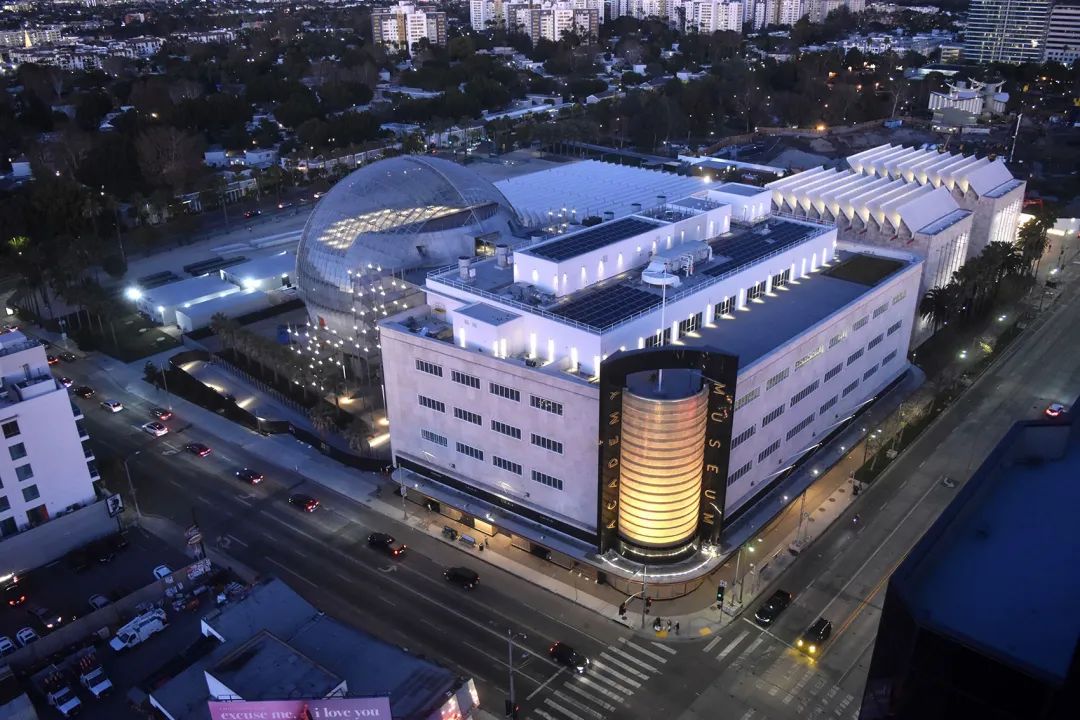
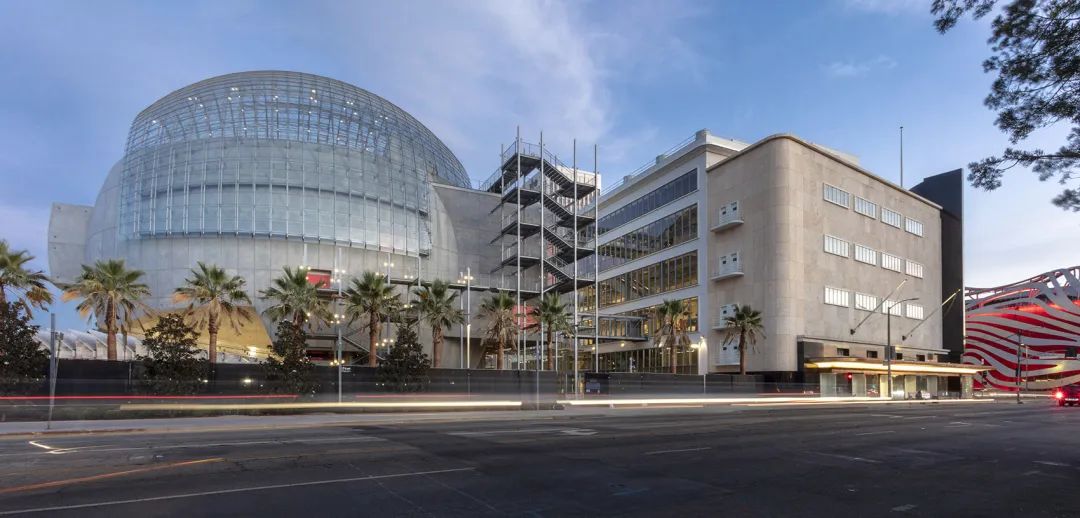
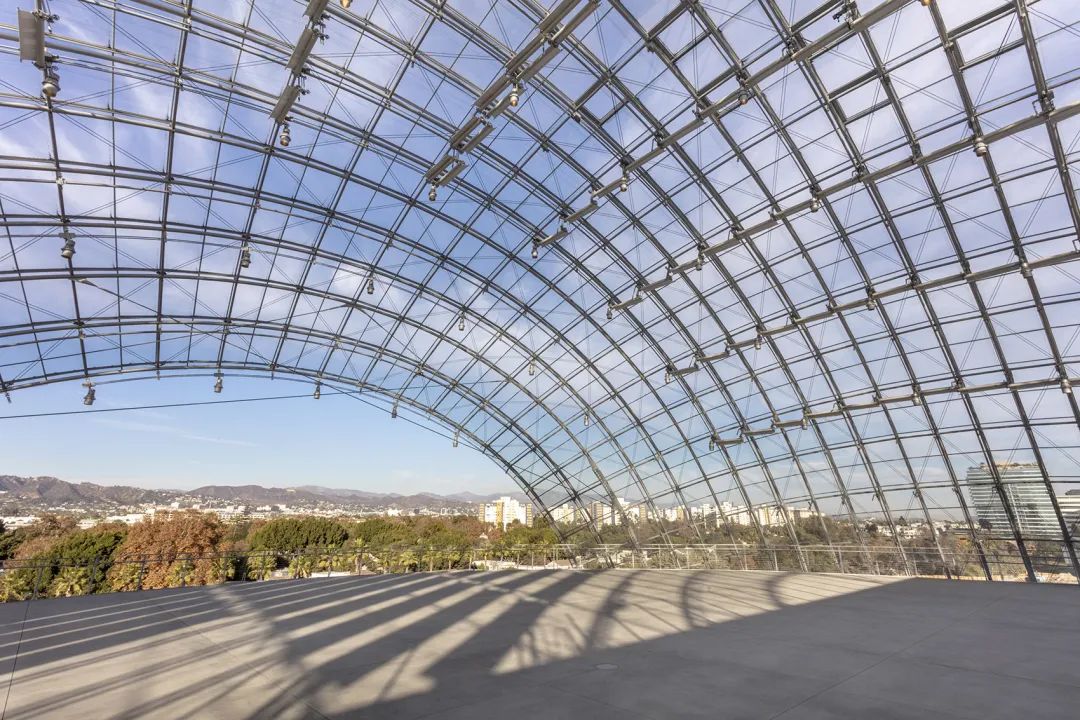
Oscar Film Museum, Los Angeles/Renzo Piano Architecture Studio
The glass dome of the building consists of 1500 customized low iron laminated tempered glass panels. These panels were cut into 146 different shapes and sizes and were manufactured by Saint-Gobain in Steyr, Austria.



03.Hot bent glass
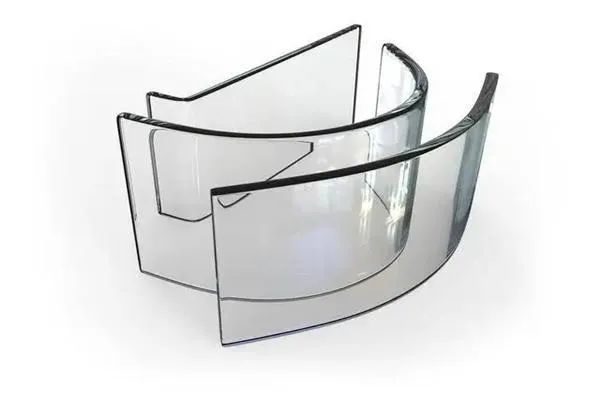

The basic principle of hot bending curved glass processing is as follows: uniformly heat the cut flat glass to a temperature of around 550 ° C (hot bending annealing) -650 ° C (hot bending tempering), at which temperature the glass becomes viscoplastic and loses its brittleness and stiffness.

The softened glass plate is placed on a mold with a specific bending form, and annealed curved glass is obtained by natural cooling after gravity deformation, or tempered curved glass is formed by mechanical pressure forming (clamping roller) and rapid cooling.
Annealed glass has better optical quality, while the optical quality of tempered curved glass formed by mechanical pressure is very sensitive to the mold.
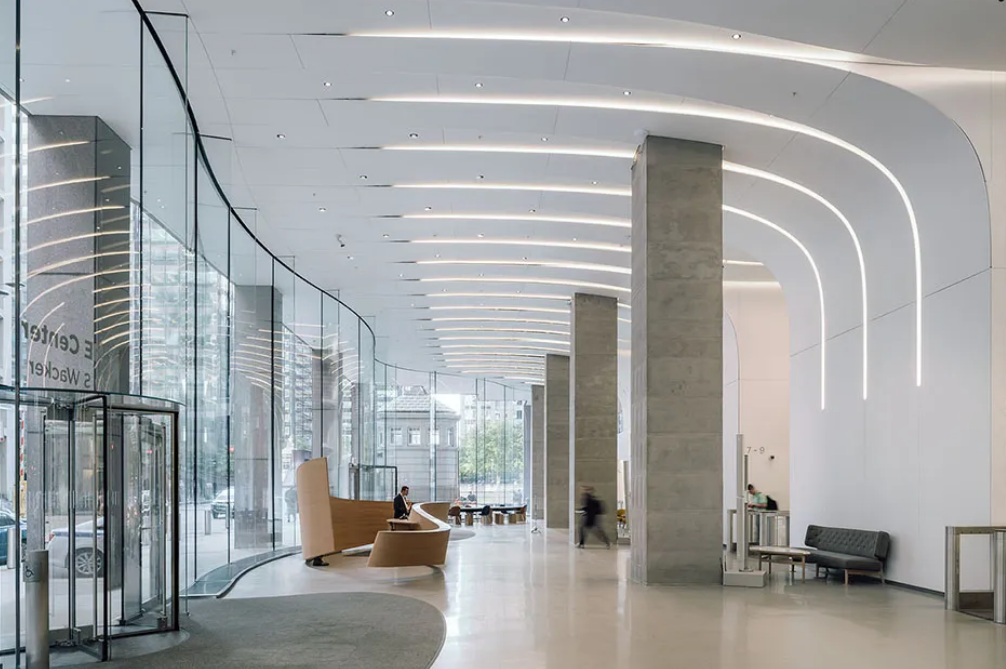

In theory, the hot bending process can obtain various surface forms through specific molds, such as the common single arc (single bend) S-curve (bend) and spherical (composite bend). For single bent glass, hot bending is relatively easy.

。Common types of bent and hot bent glass include aquarium glass and counter glass. The main technical difficulties in bending glass are the bending of straight edges and the easy occurrence of mold marks and other defects at the corners.

Composite curved glass, such as spherical glass and curved arched profiles, require a high level of technical proficiency in hot bending operations, requiring the production of accurate molds and professional hot bending furnaces to complete.
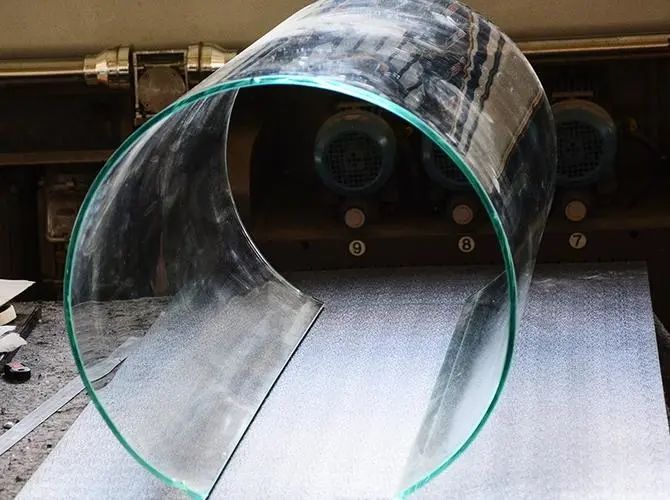
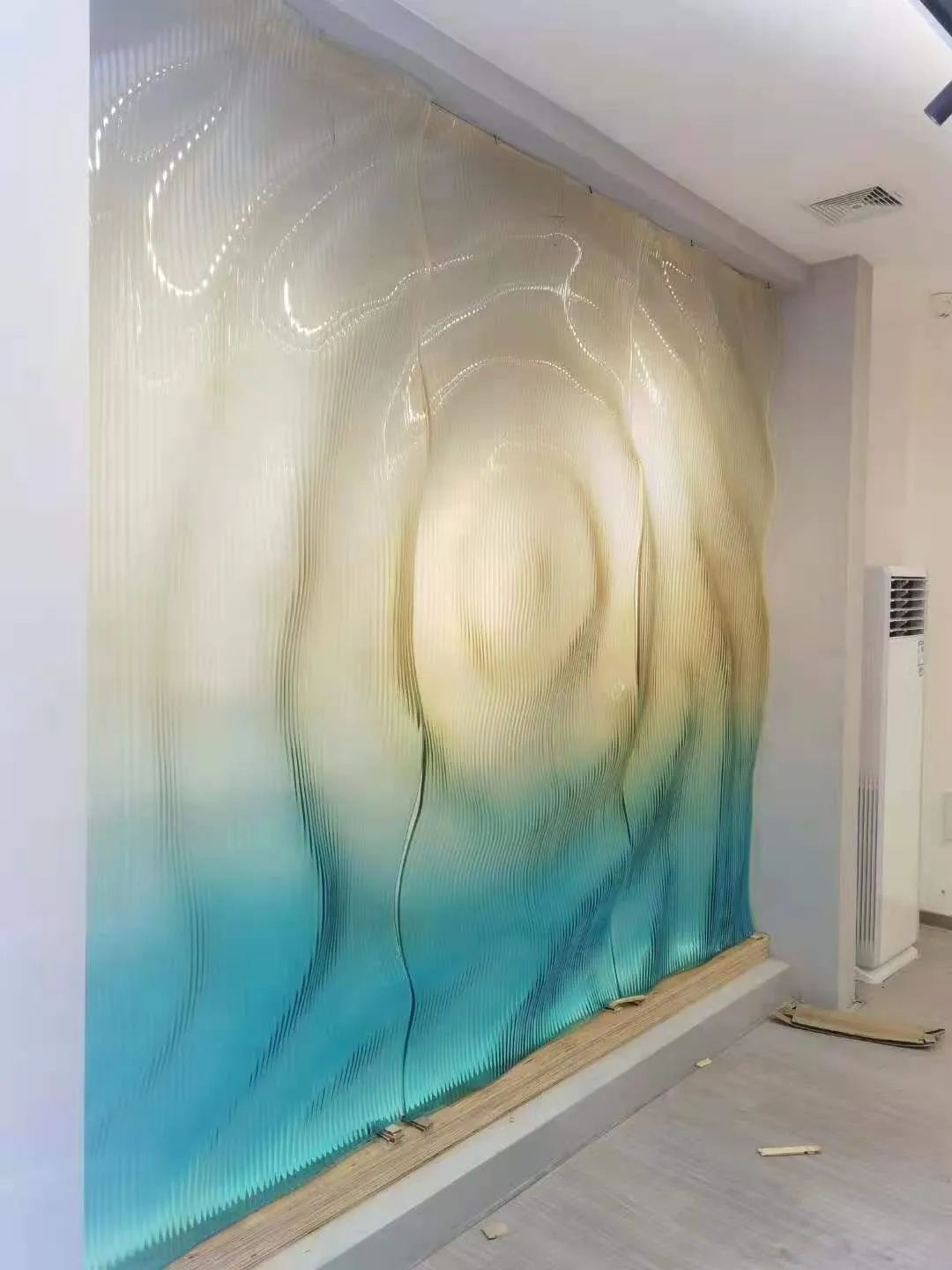
In addition, it can also achieve various complex and irregular free surface coatings, as well as flat glass printed with colored glaze. Generally, curved glass can also be hot bent, and can also be combined into Laminated glass and insulating glass.

如何判断热弯玻璃的质量How to judge the quality of hot bent glass
1. It is best to have no pits or mold marks on the surface of the glass, or to have extremely slight marks;
2. "Mirror" imaging requires that the flat part does not deform, and the curved part undergoes regular deformation;
3. Viewing objects through glass requires clarity and no local deformation;
4. Whether the annealing is in place requires that the finished product can also be cut, drilled, and other secondary processing without "self explosion";
5. Specification and size error parameters, radian comparison error ≤ 2mm, flatness error s1mm.
Application Restrictions
Mainly due to the high cost of construction and transportation. Single bends are more common in early applications. In recent years, there have also been customized cases of rich surfaces.
Related Cases
Nordstrom flagship store in New York City
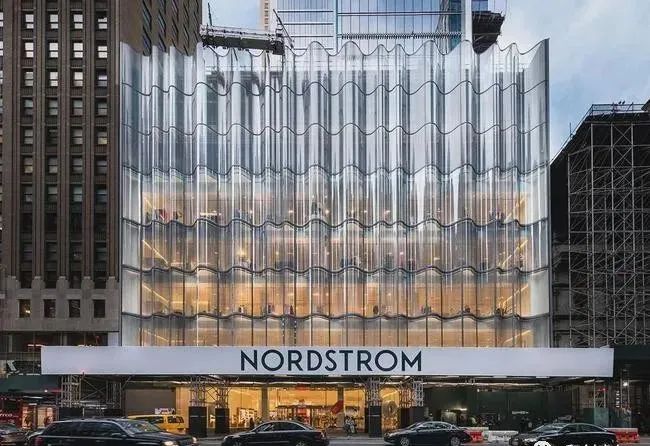
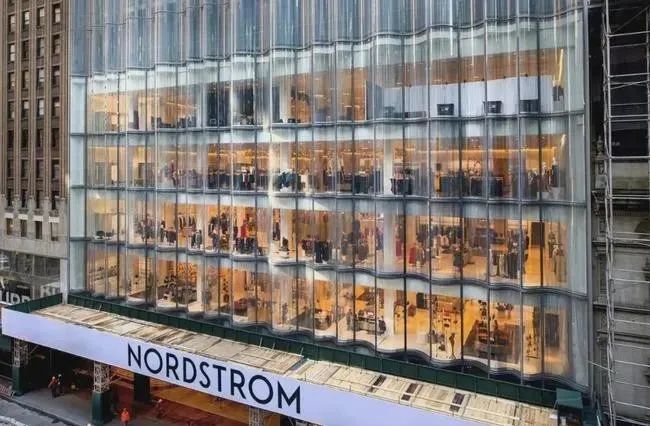
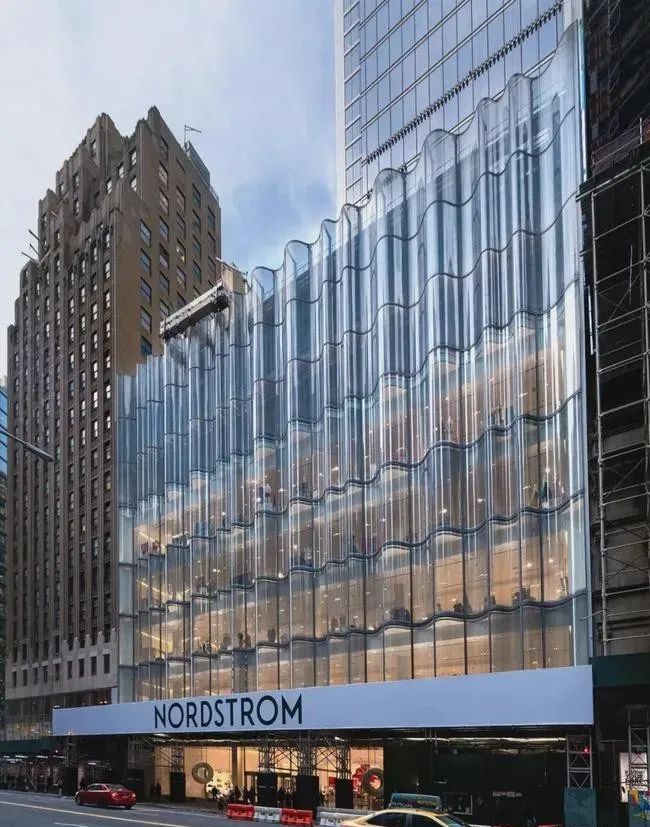
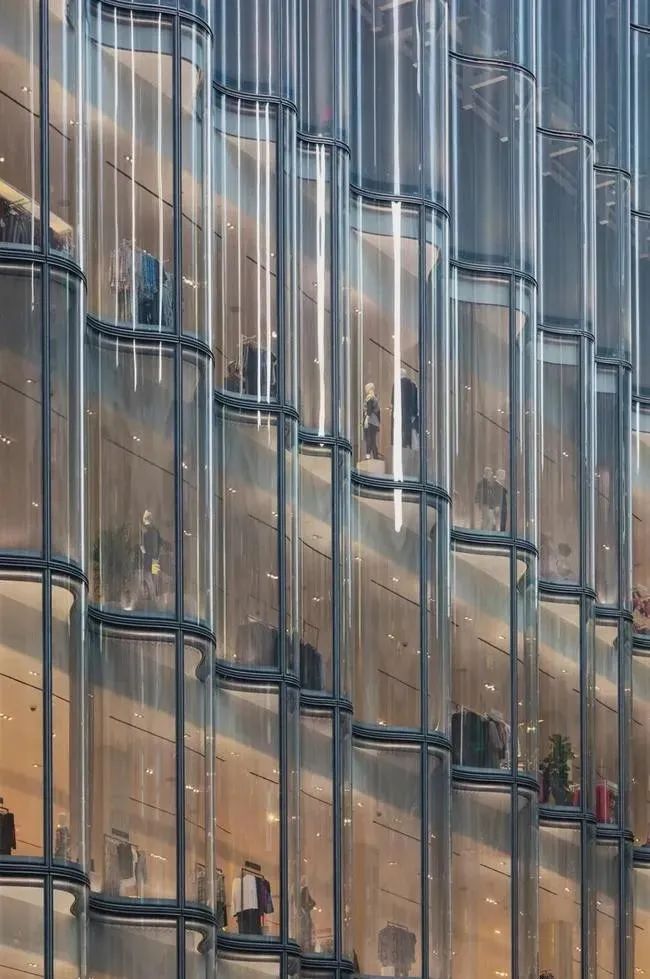




▲Super large hyperbolic hot bending glass
04.Colored Glazed Glass
Colored glazed glass is a decorative glass product that prints inorganic glaze (also known as ink) onto the surface of the glass, and then undergoes drying, tempering, or thermal processing to permanently sinter the glaze onto the glass surface, resulting in wear resistance, acid resistance, and alkali resistance.
Colored glazed glass used in architecture generally uses regular geometric patterns such as dots and lines.
。These well designed patterns can showcase a simple and elegant style in the building and space. In some cases, the use of double-layer geometric pattern overlays creates rich visual illusions.
▲Colored Glazed Glass Construction OJZFZ
Colored glazed glass is permanently sintered on the surface of the glass, with advantages such as acid and alkali resistance, corrosion resistance, never fading, safety, and high strength. It also has characteristics such as reflection and non perspective, low cost, and easy installation.
Related Cases
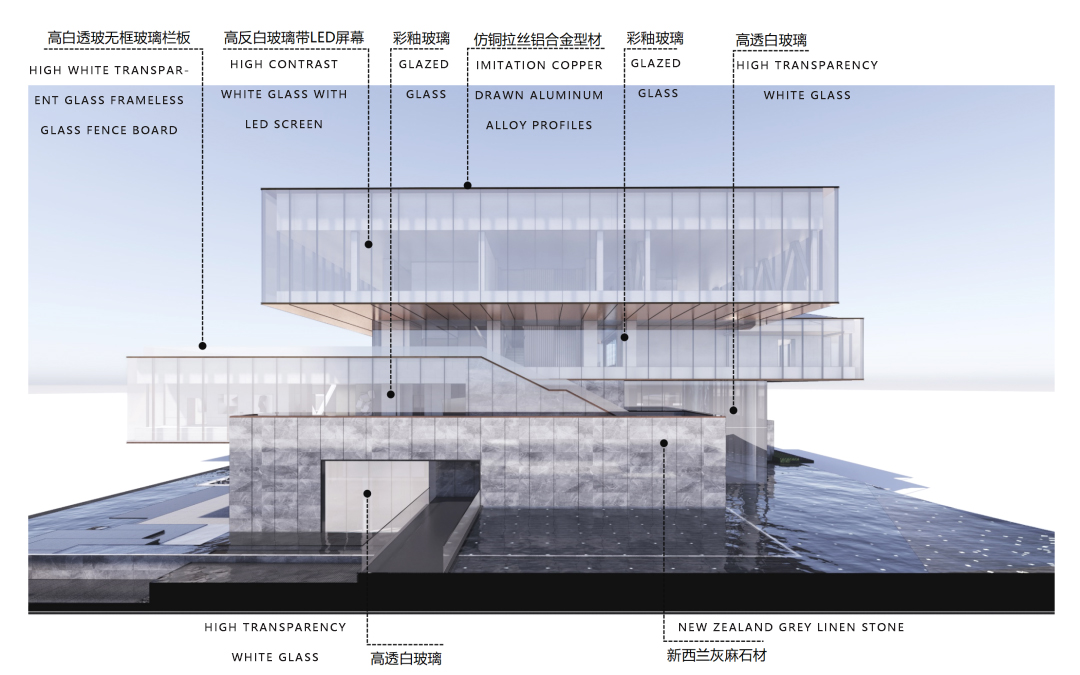
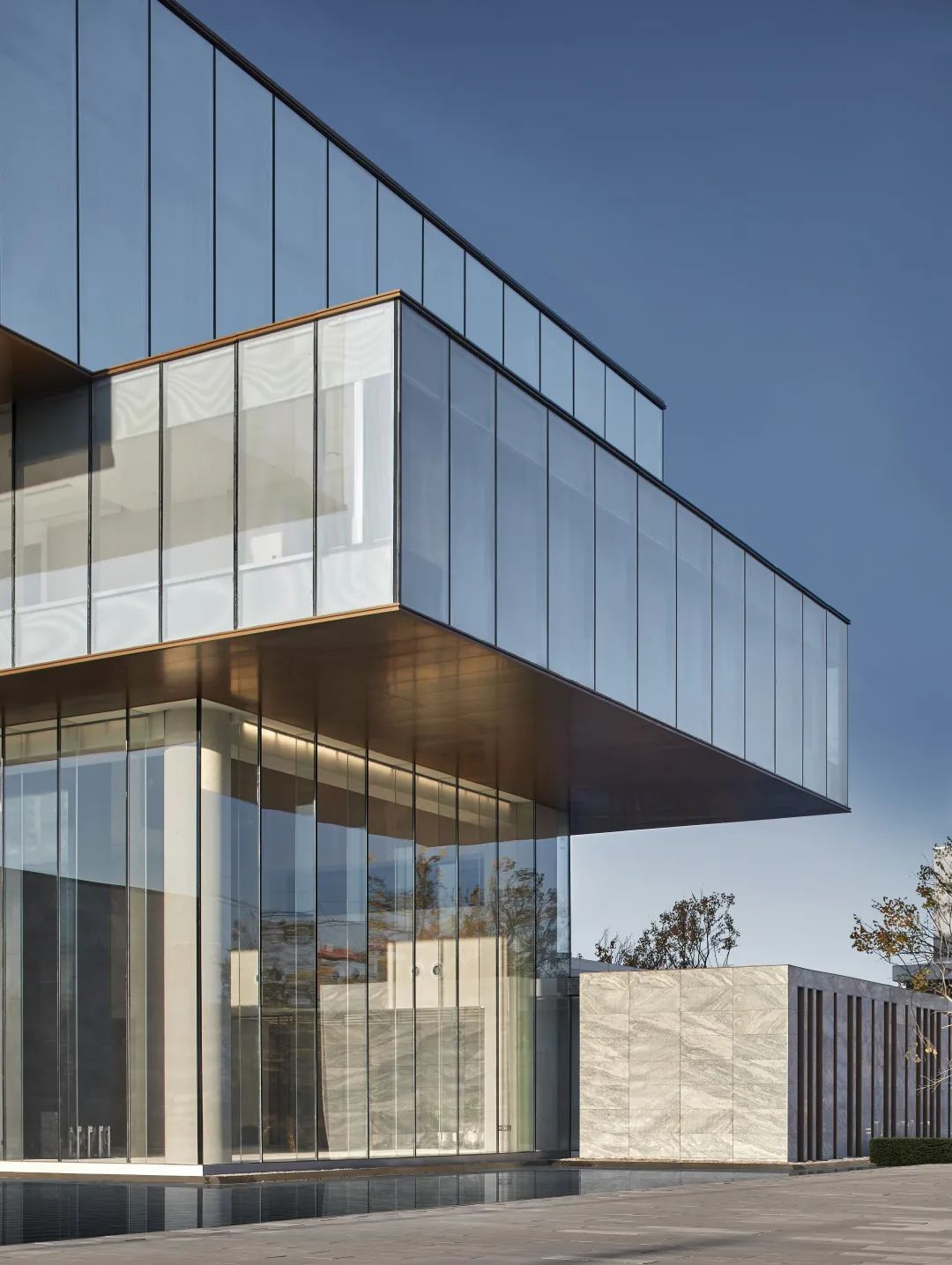
Shenyang Jindi Rongchuang. Capital Science and Technology Innovation City
In order to reduce the pressure caused by volume, a combination of New Zealand gray linen stone, high transparency white glass, and colored glazed glass was chosen in the use of materials. The collision of large color blocks of gray and white exudes elegant charm from the center of the venue without losing its tension.

▲Photography: pure point Architectural photography, Dicheng Media
▲Schematic diagram

▲Photography: pure point Architectural photography, Dicheng Media

▲Photography: pure point Architectural photography, Dicheng Media
05.Tempered glass
Tempered glass is the physical toughening of another kind of safety glass besides Laminated glass. Usually refers to heating ordinary annealed glass to a certain temperature (usually 650-700C) for quenching when the glass is close to softening. A compressive stress layer is formed on the glass surface to improve the mechanical strength and thermal impact strength of the glass.
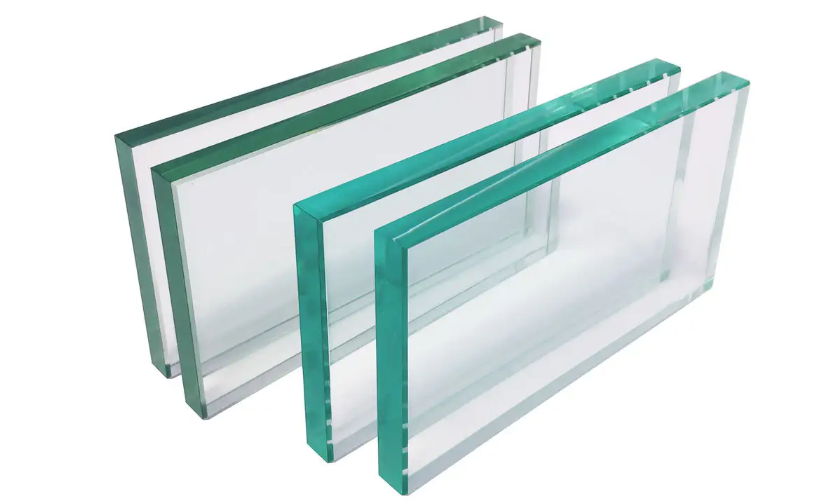

In addition, glass also has chemical tempering (also known as ion exchange tempering), which utilizes the migration and diffusion of ions on the glass surface. Through ion exchange, compositional changes occur in the thinner glass surface layer area, thereby increasing the compressive stress on the glass surface.

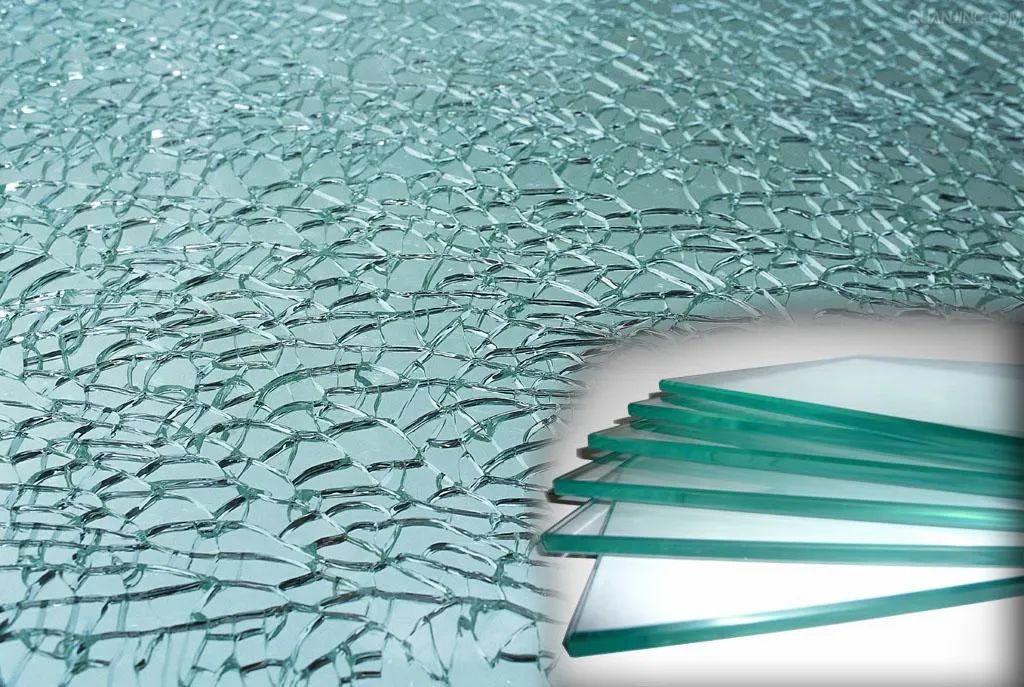
The strength of tempered glass is more than four times that of ordinary annealed glass, and its bending and impact strength has also been significantly improved. However, due to the uniform compressive stress on the outer surface of tempered glass and the corresponding tensile stress inside, once tempered, no cutting, grinding or other processing can be carried out, otherwise it will break due to the disruption of the uniform compressive stress balance.

Related Cases
Cloud Valley TOD, Hangzhou! Stacked architecture
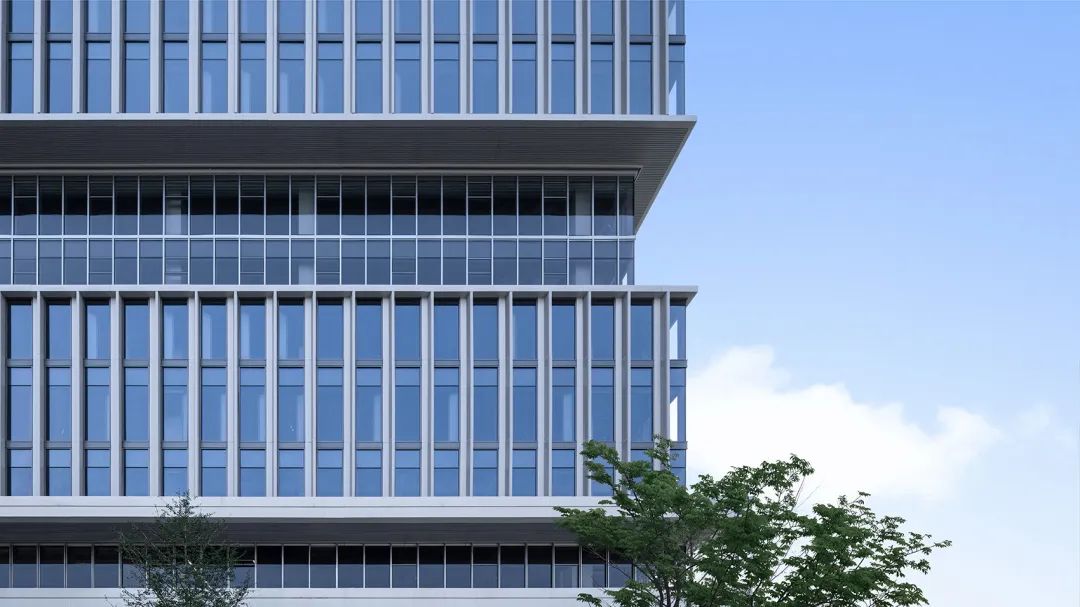
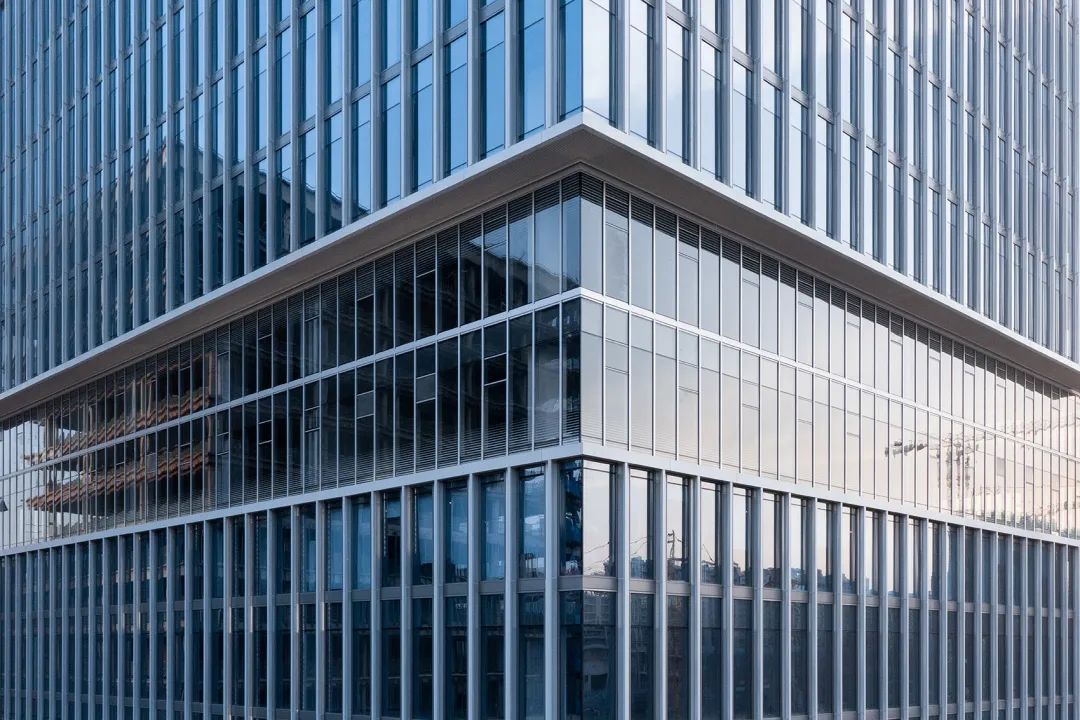
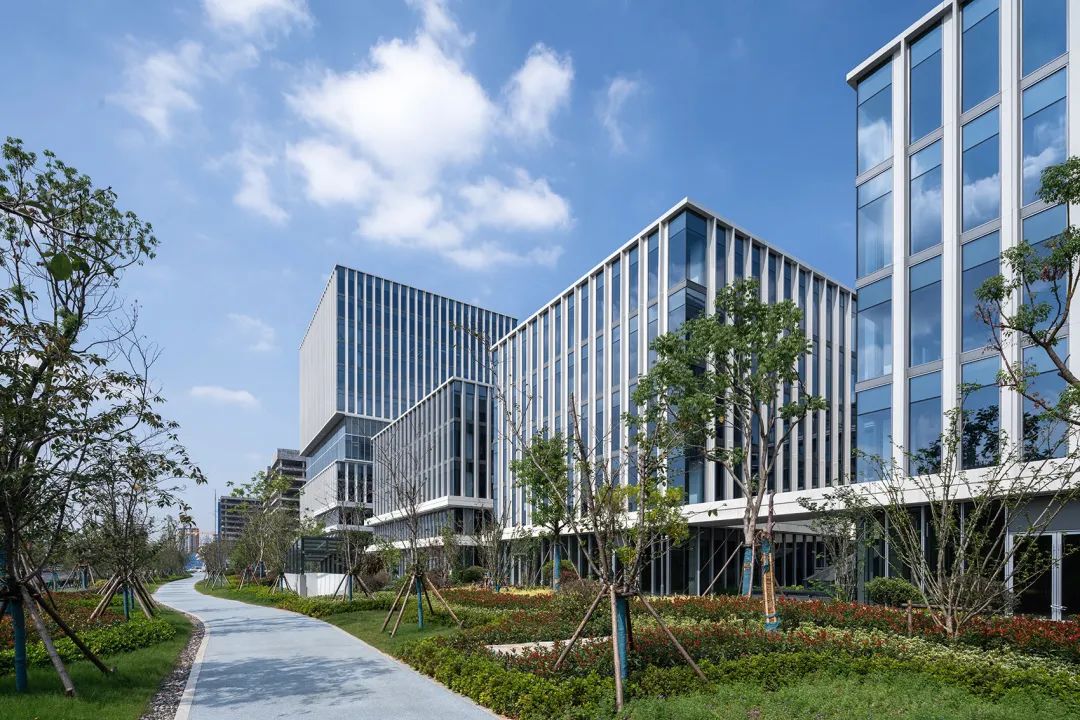
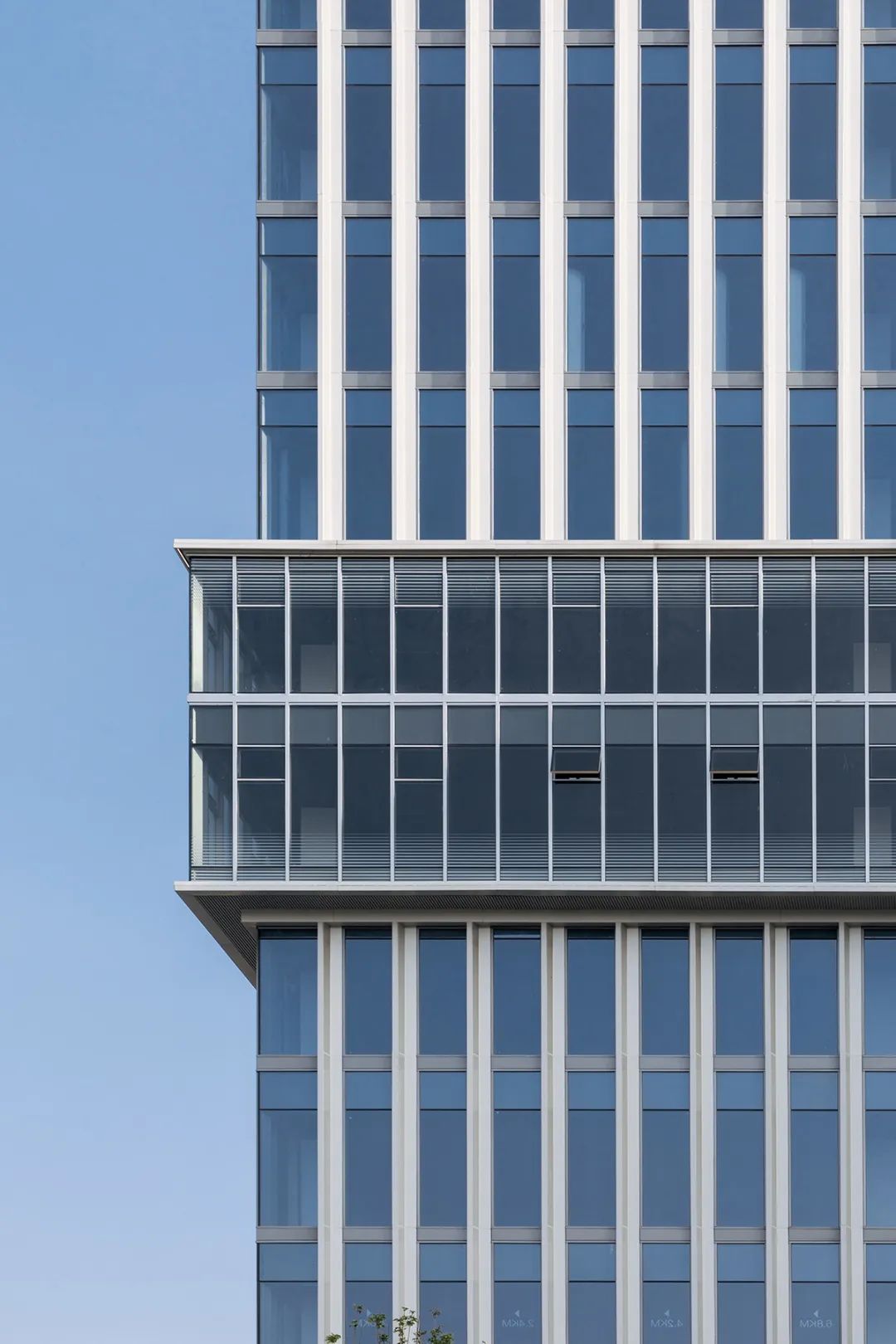




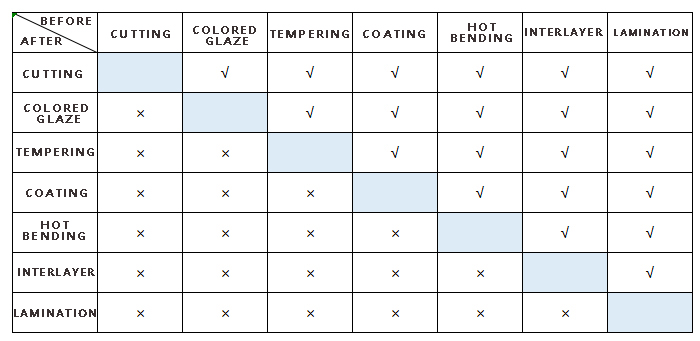
06.Sequence of Glass Deep Processing Process
Due to the changes in physical and chemical properties caused by various deep processing processes of glass, there is a certain order relationship between them. The table lists the order and feasibility of each processing process for your reference.
Article transferred from design materials